In the intricate tapestry of women’s health, one term resonates with perplexity and concern, “PCOS”. And if you are thinking that, does everything need to be known? Then the answer is “Yes”. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is a hormonal disorder that has become increasingly prevalent, affecting millions of women worldwide. Understanding this multifaceted condition is crucial for those grappling with its challenges, and for that matter, this comprehensive guide will delve into the depths of PCOS, exploring its causes, symptoms, treatments, and its profound impact on fertility.
What is PCOS?
PCOS, or Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, is a common endocrine disorder characterized by an imbalance in reproductive hormones. This imbalance leads to a range of symptoms, affecting the ovaries’ ability to function normally. The hallmark signs include irregular periods, cysts on the ovaries, and elevated levels of androgens, the so-called male hormones.
What are the First Signs of PCOS?
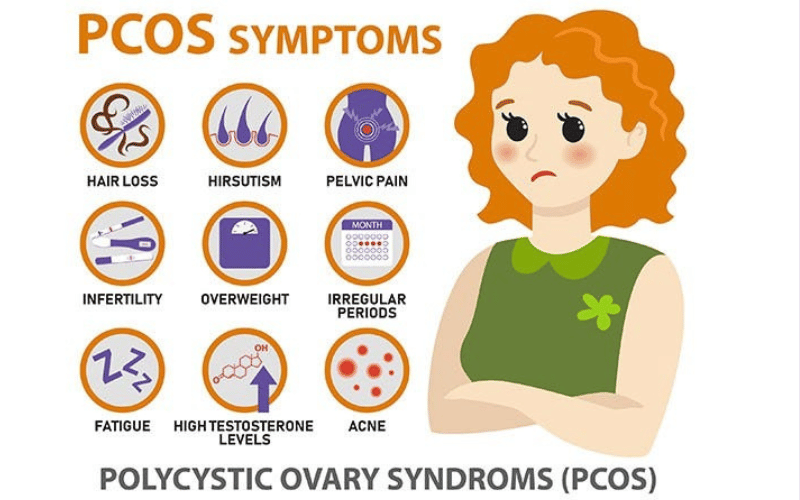
Recognizing the initial signs of this issue is pivotal for early intervention. Irregular menstrual cycles, unexplained weight gain, acne, and excessive hair growth are common indicators. Understanding these early warning signals empowers individuals to seek medical advice promptly, preventing potential complications.
To be diagnosed with this problem, a woman must exhibit at least two out of three criteria: irregular periods, signs of high androgen levels, and the presence of cysts on the ovaries. These PCOS criteria provide a diagnostic framework, allowing healthcare professionals to identify and address the condition promptly.
① Irregular Menstrual Cycles:
One of the primary indicators of this problem is irregular menstrual cycles. Women with this problem often experience unpredictable periods, characterized by variations in cycle length and the absence of menstruation for extended periods. Tracking menstrual patterns can provide valuable insights into hormonal imbalances that may underlie this problem.
② Unexplained Weight Gain:
Unexplained weight gain can be another subtle yet significant sign. Hormonal imbalances associated with this problem can impact metabolism, leading to weight gain, especially around the abdomen. Individuals noticing persistent weight changes, despite maintaining a healthy lifestyle, should consider consulting a healthcare professional to explore potential underlying causes.
③ Acne Breakouts:
Skin concerns, particularly acne, are common among women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Elevated androgen levels contribute to increased sebum production, leading to acne breakouts. While acne alone may not be indicative of this issue, its presence in conjunction with other symptoms warrants attention and evaluation.
④ Excessive Hair Growth (Hirsutism):
Excessive hair growth, known as hirsutism, is another telltale sign. Androgen dominance can result in the growth of coarse, dark hair in areas where men typically grow hair, such as the face, chest, and back. This symptom can be distressing for many women and often prompts them to seek medical advice.
Understanding and recognizing these PCOS symptoms empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward managing their health effectively. Early intervention not only aids in symptom control but also mitigates the risk of potential complications associated with untreated Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals and adopting a holistic approach to wellness are crucial steps on the journey to managing this problem and achieving optimal reproductive health.
What are the PCOS Causes?
The precise origins of this problem remain elusive, but a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors contributes to its development. Insulin resistance, hormonal imbalances, and inflammation are integral components of this puzzle. A sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary choices, and stress can further exacerbate the condition.
Ⓐ Genetic Influences:
While the exact genetic factors triggering this issue are not fully understood, there is evidence of a familial predisposition. Women with a family history of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome may have a higher likelihood of developing the condition. Researchers are actively exploring the interplay of specific genes that may contribute to the manifestation of this problem.
Ⓑ Environmental Factors:
Beyond genetics, environmental influences play a role in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome development. Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals and toxins may impact hormonal balance, potentially contributing to the onset of this problem. Understanding and minimizing exposure to these environmental factors is an ongoing area of research in the quest to unravel the complexities of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome causation.
Ⓒ Insulin Resistance:
One of the pivotal factors in PCOS causes is insulin resistance. Insulin, a hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar, may face resistance in women with this issue. This resistance leads to elevated insulin levels, triggering the overproduction of androgens, such as testosterone. The resulting hormonal imbalance contributes to irregular menstrual cycles and other PCOS symptoms.
Ⓓ Hormonal Imbalances:
Hormonal disruptions lie at the heart of this problem. Elevated levels of androgens, often referred to as male hormones, disturb the delicate balance needed for normal ovarian function. This hormonal imbalance not only interferes with regular ovulation but also manifests in physical symptoms like acne, hirsutism (excessive hair growth), and male-pattern baldness.
Ⓔ Inflammation:
Inflammation is another key player in the Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome puzzle. Chronic inflammation can exacerbate insulin resistance and contribute to the progression of the disorder. Research suggests that inflammatory markers are elevated in women with this issue, emphasizing the intricate connection between inflammation and hormonal irregularities in the manifestation of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome.
Ⓕ Lifestyle Factors:
The modern lifestyle, characterized by sedentary habits, poor dietary choices, and high-stress levels, has been implicated in the exacerbation of this problem. Sedentary behavior can contribute to weight gain, which, in turn, amplifies insulin resistance. Poor dietary choices, especially a diet rich in processed foods and sugars, may further contribute to hormonal imbalances.
PCOS Treatment:
Addressing this problem involves a multifaceted approach tailored to individual needs. Lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, form the foundation. Hormonal contraceptives can help regulate menstrual cycles, while anti-androgen medications manage symptoms like acne and excessive hair growth. Here’s a closer look at the multifaceted approach for PCOS treatment, encompassing lifestyle modifications and medical interventions:
‣ Lifestyle Modifications:
• Balanced Diet:
Adopting a balanced diet is pivotal in managing Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Emphasize whole foods, lean proteins, and complex carbohydrates while minimizing processed sugars. This helps regulate blood sugar levels and mitigate insulin resistance, a common factor in this issue.
• Regular Physical Activity:
Engaging in regular physical activity is a cornerstone of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome management. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, aids in weight management, and promotes overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, tailored to individual fitness levels.
• Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for women with this problem, as excess body weight can exacerbate hormonal imbalances. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can significantly improve symptoms and enhance reproductive outcomes.
‣ Hormonal Contraceptives:
• Oral Contraceptives:
Birth control pills containing estrogen and progestin are commonly prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles in women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. These contraceptives help establish a predictable menstrual pattern, reducing the risk of endometrial hyperplasia (overgrowth of the uterine lining) associated with irregular periods.
• Hormonal Regulation:
By maintaining hormonal balance, oral contraceptives alleviate symptoms such as irregular periods, acne, and excessive hair growth. They provide a valuable tool for managing the hormonal fluctuations characteristic of this problem.
‣ Anti-Androgen Medications: Managing Cosmetic Symptoms
• Managing Acne:
PCOS often leads to increased androgen levels, contributing to acne. Anti-androgen medications, such as spironolactone, can be effective in controlling acne outbreaks.
• Addressing Excessive Hair Growth:
Hirsutism, characterized by excessive hair growth in areas where men typically grow hair, is another common concern. Anti-androgens can help manage this symptom, improving both physical appearance and emotional well-being.
‣ Individualized Approach: Tailoring Treatment to Unique Needs
• Consultation with Healthcare Providers:
PCOS is a heterogeneous condition, and its manifestations vary among individuals. Consultation with healthcare providers, including gynecologists, endocrinologists, and nutritionists, is essential for crafting an individualized treatment plan.
• Monitoring and Adjustments:
Regular monitoring of symptoms, hormonal levels, and overall health allows for timely adjustments to the treatment plan. Flexibility and ongoing communication with healthcare professionals ensure that interventions remain aligned with evolving needs.
PCOS and Pregnancy:
PCOS and pregnancy, These words can feel opposite to each other, but the journey to motherhood for women with PCOS problem can be challenging but by no means impossible. With timely intervention, lifestyle adjustments, and, if necessary, fertility treatments, many women with this issue successfully conceive and carry pregnancies to term. Collaborative care between the patient, healthcare provider, and reproductive specialists is key to achieving a healthy pregnancy.
PCOS Treatment for Unmarried Women:
Unmarried women with this problem face distinct challenges, particularly concerning fertility concerns. While the primary treatment approach remains similar, a proactive approach to fertility preservation may be considered. Discussing reproductive options and potential future challenges with healthcare providers is essential for PCOS treatment for unmarried women.
Conclusion:-
PCOS is a complex, often misunderstood condition that affects women in profound ways. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can navigate the challenges with resilience. Whether contemplating pregnancy, managing symptoms, or seeking fertility assistance, a proactive and informed approach is key. For those facing infertility challenges associated with this problem, specialized assistance can make a significant difference.
Nimaaya IVF Center, with Specialist Dr. Yuvrajsingh Jadeja its expertise in infertility treatment, offers personalized solutions to navigate the complexities of fertility issues related to this problem. Their comprehensive approach encompasses advanced reproductive technologies, compassionate care, and a commitment to helping individuals build their families. With the right knowledge, support, and access to specialized care, women can reclaim control over their reproductive health and embark on the path to overall well-being.











Comments 2
Wow, this sounds promising! It’s reassuring to know that there are top-notch IVF centers in India with high success rates. As someone considering IVF, this blog gives me hope and a starting point for my research. Thank you for sharing!”
This post is extremely radiant. I really like this post. It is outstanding compared to other posts I’ve read in quite a while. Much obliged for this better-than-average post. I truly value it!