A question that is often asked but rarely discussed in depth is: What is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and how does it affect fertility? Well, buckle up, folks! This blog post aims to dissect this medical condition in simple language. We’ll learn about PID, courtesy of the expertise at India IVF Fertility. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is an essential health concern that affects countless women worldwide. As an often misunderstood and misdiagnosed condition, it is crucial to spread awareness and understanding about PID. This article aims to elucidate the causes, symptoms, treatments, and preventative measures of pelvic inflammatory disease, offering a comprehensive guide for those seeking information.
What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, commonly known as PID, is an infection of a woman’s reproductive organs. It involves the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and other adjacent structures. It usually occurs when sexually transmitted bacteria spread from the vagina to the uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries. PID starts with an infection in the cervix that travels upward, causing inflammation and infection in the upper genital tract. Mostly, PID occurs due to sexually transmitted infections (STIs) associated with gonorrhoea and chlamydia. Repeated episodes of untreated PID can lead to infertility, chronic pelvic pain, and ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the uterus). When diagnosed early, PID is treated, and most women make a full recovery.
Also Read: Discover the Top 5 IVF Centers in Ahmedabad for IVF Journey
Signs and Symptoms of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
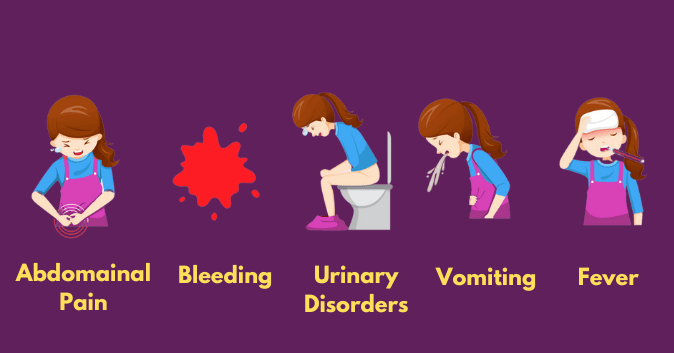
PID symptoms can vary in intensity and may not always be apparent.
In most patients infected with chlamydia, the symptoms are either mild or none, while the damage is silently done to their reproductive organs. Here are the pelvic inflammatory disease symptoms and sign:
❧ Pelvic Pain:
A persistent and often severe manifestation, pelvic pain serves as a hallmark symptom of PID, indicative of inflammation and infection within the reproductive organs.
❧ Abnormal Vaginal Discharge:
An unusual discharge with an unpleasant odor may manifest due to the infection impacting the cervical glands, presenting a distinctive symptom of PID.
Also Read: Understanding the Vagina: Functions, Health and Abnormalities
❧ Painful Urination:
Pelvic inflammation is another important symptom that can cause pain or discomfort when urinating.
❧ Irregular Menstrual Bleeding:
One notable symptom of PID is the potential for changes in menstrual patterns, such as heavier or more painful periods.
❧ Fever and Fatigue:
Systemic symptoms such as fever and fatigue may accompany PID, indicating a more widespread infection.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek prompt medical attention. In a small fraction of patients, especially those infected with gonorrhoea, the PID symptoms are often severe, with patients experiencing a high-grade fever and severe pain. PID can have a negative impact on pelvic health and result in major side effects like infertility, tubal scarring, and chronic pelvic pain if treatment is not received. You must pay attention to the unnatural behaviour of your vaginal conditions. If there is any pain or you have any issues while having sex, consult a doctor without delay.
What Causes Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease is primarily caused by untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs). PID can result from bacteria infecting the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries when these infections travel up the reproductive tract. Other potential pelvic inflammatory disease causes include delivery of a baby, abortion, or the insertion of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs).
While gonorrhoea and chlamydia are the two most common infections that cause PID, many different types of bacteria can also cause PID. You get both of these infections through unprotected sex. These two STIs cause about 90% of all PID cases.
Less commonly, the disease can also arise when the normal bacteria present in the woman’s vagina or cervix move upward into other reproductive organs coupled with additional causes such as the following.
- Childbirth.
- Pelvic surgery.
- Miscarriage.
- Getting an intrauterine device (IUD).
- Non-sexually transmitted bacteria
- Abortion
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Treatments
There are several options available for treating PID, ranging from medication to surgery. The treatment course may vary depending on the severity of the infection and the underlying cause of the disease. Here are the various treatment options available for PID:
☑ Antibiotic Therapy:
Administering broad-spectrum antibiotics is the primary approach to targeting and eliminating the bacteria causing the infection. Completion of the full antibiotic course is crucial for ensuring complete eradication.
☑ Pain Management:
One important part of treatment for pelvic pain and discomfort may involve the recommendation of over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers.
☑ Rest and Recovery:
Adequate rest is important during treatment, allowing the body to recover. Avoiding sexual activity until the infection clears is crucial to preventing reinfection.
☑ Partner Treatment:
If STDs are the main cause of PID, testing and treatment for sexual partners are necessary to stop the infection from returning.
☑ Hospitalisation:
Hospitalization may be required in severe cases of PID. If the patient experiences complications like an abscess or a burst fallopian tube, or if their condition does not improve after the first round of antibiotics, hospitalization is advised. In the hospital, the patient will be given painkillers and intravenous (IV) antibiotics.
A woman may also be advised to get treated in the hospital, if:
- She is pregnant
- She is seriously ill
- Her symptoms do not improve with oral antibiotics even after a few days, and you need antibiotics intravenously
- She has a suspected abscess in a fallopian tube or ovary
- She needs surgery (in rare situations)
☑ Surgery:
Women with HIV or those at high risk for complications may require more aggressive treatment, including surgical intervention. Surgery is the last treatment option for PID. It is usually recommended if an abscess needs to be drained or the infection has spread to other parts of the reproductive system.
☑ Follow-Up Care:
To track progress, follow-up visits with medical professionals are required regularly. They take care of any residual symptoms and guarantee that the infection is completely resolved.
Infertility can result from postponing PID treatment, which can permanently harm the reproductive organs. Pelvic health plays a crucial role in overall reproductive health, and it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately at the first sign of any symptoms
Also Read: Exploring the Top 5 IVF Centers in Surat for Successful IVF Journey
Who is Diagnosed with Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
See your doctor straight away if you experience pelvic inflammatory disease symptoms. Your chances of receiving successful treatment increase with the time you receive care.
If you experience lower abdominal pain, your physician or nurse will look for:
- unusual discharge coming from your cervix or vagina
- A pus-filled abscess close to your fallopian tubes or ovaries
- sensitivity or discomfort in your ovaries
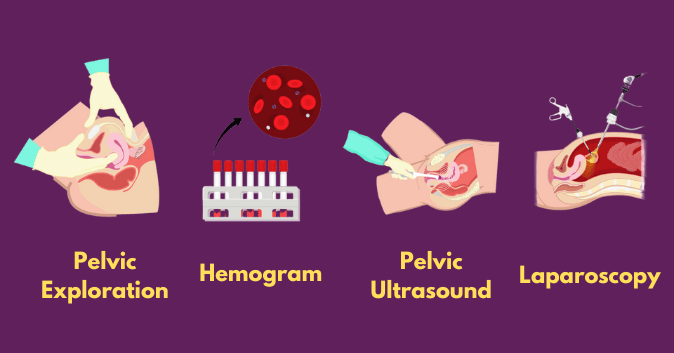
There isn’t one specific test for PID. Usually, your healthcare provider can diagnose PID through:
- Ask about your sexual activity, general health, and symptoms, as well as your medical history.
- a pelvic exam to check your reproductive system and feel for sore spots or pus-filled collections called abscesses.
- a vaginal culture to check for specific bacteria in your vaginal discharge.
Other tests might need to be done to diagnose PID
- Blood tests.
- Urine test to check out a urinary tract infection
- Ultrasound to get clearer images of your reproductive system.
- Testing for STIs.
Sometimes, your provider may recommend:
- Endometrial biopsy: Your doctor takes a small sample of tissue from the lining of your uterus and examines it for illnesses.
- Laparoscopy: Your provider makes small incisions in your pelvis, then inserts a lighted instrument to look more closely at your reproductive organs.
or a different problem that looks like PID. These can include:
- Tests for STIs, especially gonorrhea and chlamydia. These infections can cause PID.
- A test for a urinary tract infection or other conditions that can cause pelvic pain
Also Read: Filtering the Top 5 IVF Centers in Vadodara for Successful IVF Journey
How to Prevent Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Sometimes, PID isn’t due to a sexually transmitted infection. It can come from normal vaginal bacteria traveling to your reproductive organs. Avoiding douching may lower the risk.
Take steps to practice safe sex. The following are some strategies to shield oneself from STIs that can result in PID:
‣ Limiting sexual partners:
The more partners you have, the higher your risk.
‣ Choosing barrier methods of birth control:
Diaphragms and condoms are examples of these birth control methods. Combine a barrier method with spermicide, even if you take birth control pills.
‣ Seeking treatment if you notice symptoms:
Symptoms include unusual vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, or bleeding between periods.
‣ Getting regular checkups:
Have regular gynecological exams and screenings. Cervical infections are frequently detectable and treatable before they spread to other reproductive organs.
Also Read: A Comprehensive Guide to Cervical Cancer
‣ Healthy hygiene habits:
Maintaining good hygiene can also help stop PID from happening. To prevent bacteria from moving from the anus to the vagina, women should, for example, always wipe after using the loo from front to back. Additionally, people should avoid using douches because they may upset the normal bacterial balance in the vaginal region, increasing the risk of infection.
‣ Request that your partner be tested:
Get your partner tested and treated if you have STIs or pelvic inflammatory disease. This may stop the transmission of STIs and the potential recurrence of PID.
‣ Don’t douche:
Douching upsets the balance of bacteria in your vagina.
Risk Factors of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Several factors could raise your risk of developing pelvic inflammatory disease, such as:
- being under 25 years old and engaging in sexual activity
- Having more than one sexual partner
- engaging in sexual activity with a person who has multiple partners
- using a condom when having sex
- Regular douching can conceal symptoms by upsetting the delicate balance of beneficial versus harmful bacteria in the vagina.
- Having a history of sexually transmitted infections or pelvic inflammatory disease
After the implantation of an intrauterine device (IUD), there is a slight increase in the risk of PID. Usually, this risk is limited to the first three weeks following insertion.
Conclusion
I hope this blog has helped you understand and get an idea about Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) better, especially concerning its implications for infertility treatment. Remember, prevention, early detection, and proper treatment are the keys to dealing with PID, particularly for those seeking infertility treatment. At Nimaaya IVF Center, our expert professionals are experienced in diagnosing and providing treatment for pelvic inflammatory disease, recognizing its significance in the context of infertility treatment. While there is no single test to diagnose PID, our doctors will diagnose you based on your symptoms and a gynecological examination, ensuring comprehensive care, especially for those undergoing infertility treatment. Schedule an appointment with us to ensure you get a prompt diagnosis and treatment if needed, particularly if you’re considering infertility treatment options.