Introduction
Male infertility is a topic often shrouded in silence and stigma, yet it affects millions of couples worldwide. While infertility is commonly associated with female factors, it’s crucial to recognize that male infertility plays an equally significant role in conception challenges. Understanding male infertility symptoms is pivotal for couples navigating the journey towards parenthood. In this article, we delve into the complexities of male infertility causes and symptoms, and potential treatments. Whether you’re experiencing difficulties conceiving or simply seeking knowledge on this topic, read on to gain insights into the infertility of males and its implications.
Male Infertility Symptoms Unveiled
Male infertility symptoms often fly under the radar, overshadowed by the spotlight on female fertility challenges. However, they are crucial indicators of underlying reproductive health issues. Understanding infertility symptoms for males, also known as male factor infertility symptoms, is vital for early detection and intervention. Let’s delve into the subtle signs and glaring indicators that unveil male infertility:
❧ Changes in Sexual Function:
One of the primary male infertility symptoms manifests in alterations in sexual function. This may include difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection, premature ejaculation, or reduced libido. While these issues can stem from various factors, they can also be indicative of underlying fertility concerns.
❧ Abnormalities in Ejaculation:
Another telltale sign of male factor infertility is abnormalities in ejaculation. This may present as retrograde ejaculation, where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the urethra during ejaculation. Additionally, experiencing pain or discomfort during ejaculation warrants attention and evaluation by a healthcare professional.
❧ Testicular Abnormalities:
Physical abnormalities or discomfort in the testicular region can signal potential fertility issues. These may include swelling, lumps, or pain in the testicles. Such abnormalities may indicate problems with sperm production or sperm transport, necessitating further investigation.
❧ Changes in Semen Quality:
Semen analysis is a crucial diagnostic tool for assessing male fertility. Changes in semen quality, such as decreased sperm count, poor sperm motility, or abnormal sperm morphology, are indicative of male infertility. Monitoring semen parameters through routine analysis can provide valuable insights into fertility status.
❧ Hormonal Imbalances:
Hormonal imbalances can disrupt the delicate interplay necessary for optimal reproductive function. Symptoms such as decreased facial or body hair, gynecomastia (enlarged breast tissue), or unexplained weight gain may signal underlying hormonal issues impacting fertility.
❧ Underlying Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions can contribute to male infertility symptoms. Conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, or infections affecting the reproductive organs can impair fertility. Identifying and managing these underlying health issues is crucial for optimizing fertility potential.
❧ Environmental and Lifestyle Factors:
Environmental and lifestyle factors play a significant role in male fertility. Exposure to toxins, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, or illicit drug use can impair sperm production and function, resulting in male infertility symptoms.
Male infertility symptoms, often intertwined with broader health indicators, warrant thorough evaluation and attention. Consulting with a healthcare provider specializing in reproductive health, such as those at Nimaaya IVF Center, can facilitate comprehensive assessment and personalized treatment planning. By recognizing and addressing male infertility symptoms proactively, individuals can take proactive steps toward achieving their fertility goals.
What are the Major Male Infertility Cuses?
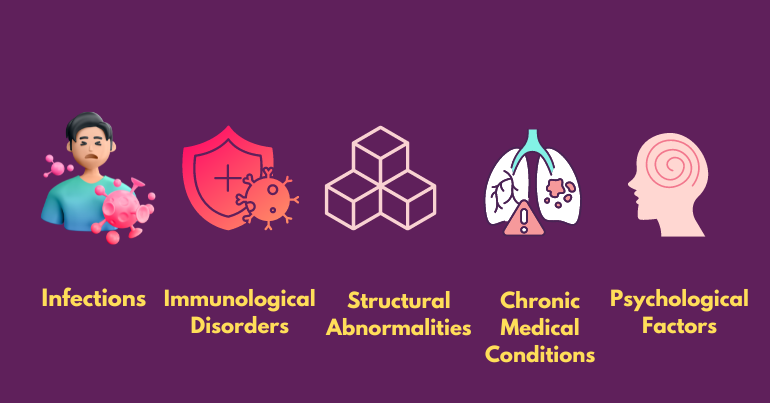
Male infertility, a complex and often overlooked issue affects millions of men worldwide, presenting a myriad of challenges on the path to parenthood. Delving into the intricacies of male reproductive health reveals a multitude of factors that can contribute to infertility. From physiological abnormalities to environmental exposures and lifestyle choices, understanding the major causes of male infertility is paramount in addressing fertility concerns effectively. By unraveling the underlying factors that impact male fertility, individuals and healthcare providers can devise targeted interventions to optimize reproductive outcomes and facilitate the journey toward conception.
‣ Infections:
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, or HIV can lead to inflammation of the reproductive organs, resulting in scarring or blockages that impede sperm transport. Additionally, non-sexually transmitted infections such as mumps orchitis, a complication of the mumps virus, can cause inflammation of the testicles and compromise sperm production.
‣ Immunological Disorders:
In some cases, the immune system may mistakenly target sperm cells as foreign invaders, producing antibodies that impair sperm motility or function. Immune-mediated infertility can occur following trauma, surgery, or vasectomy reversal, where sperm antigens are exposed to the immune system.
‣ Structural Abnormalities:
Congenital or acquired structural abnormalities of the reproductive tract can hinder sperm production, transport, or ejaculation. Conditions such as hypospadias (abnormal placement of the urethral opening), ejaculatory duct obstruction, or urethral strictures can interfere with normal reproductive function and fertility.
‣ Chronic Medical Conditions:
Underlying chronic medical conditions such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, or autoimmune disorders can negatively impact male fertility by disrupting hormonal balance, impairing blood flow to the reproductive organs, or inducing systemic inflammation. Poorly managed chronic illnesses can exacerbate infertility issues and affect overall reproductive health.
‣ Psychological Factors:
Psychological stress, anxiety, or depression can have a profound impact on male fertility by altering hormonal levels, reducing libido, or affecting sexual function. Relationship problems, performance anxiety, or unresolved trauma may also contribute to erectile dysfunction or ejaculatory disorders, thereby impacting fertility outcomes.
‣ Heat Exposure:
Prolonged exposure to excessive heat can adversely affect sperm production and quality. AcFrequentot tub use, prolonged sitting, or occupational exposure to high temperatures (e.g., working in hot environments or using heated machinery) can elevate scrotal temperatures and impair spermatogenesis.
‣ Prescription Drug Side Effects:
Certain medications, including chemotherapy drugs, antipsychotics, antiandrogens, and some antibiotics, can have adverse effects on male fertility as a side effect. These medications may disrupt hormonal balance, interfere with sperm production, or cause ejaculatory dysfunction, leading to temporary or permanent infertility.
By considering these additional causes of male infertility alongside the previously mentioned factors, healthcare providers can conduct a comprehensive evaluation to identify underlying issues and tailor treatment plans accordingly. Early detection and intervention are essential for optimizing fertility outcomes and addressing male infertility effectively.
Exploring the Different Types of Male Infertility
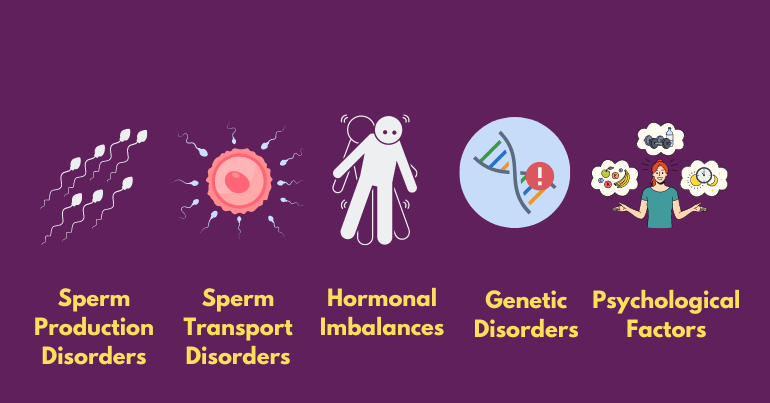
Male infertility can arise from various factors, which can be broadly categorized into several types. These factors may interact in complex ways, making the diagnosis and treatment of male infertility a multifaceted and individualized process.
1. Sperm Production Disorders:
Sperm production disorders encompass conditions such as azoospermia, characterized by the absence of sperm in semen, and oligospermia, which denotes a low sperm count. These disorders can stem from hormonal imbalances, genetic abnormalities, or environmental factors, necessitating thorough evaluation and tailored treatment approaches.
‣ Azoospermia:
Azoospermia, characterized by the absence of sperm in semen, can result from obstructive or non-obstructive causes within the male reproductive system. Diagnosis typically involves thorough examination and testing to identify the underlying reason for the absence of sperm, guiding treatment options, and interventions.
‣ Oligospermia:
Oligospermia is characterized by a low sperm count, typically defined as fewer than 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen. This condition can significantly reduce the chances of conception and may require medical intervention for fertility treatment.
‣ Teratospermia:
Teratospermia refers to the condition characterized by abnormal sperm morphology, where the shape of sperm deviates from the typical structure. This can impact fertility by reducing the sperm’s ability to effectively penetrate and fertilize an egg.
‣ Asthenospermia:
Asthenospermia refers to a condition characterized by reduced sperm motility, impacting the ability of sperm to move effectively toward the egg for fertilization. This condition can significantly decrease the chances of natural conception and may require assisted reproductive techniques for successful fertilization.
2. Sperm Transport Disorders:
Conditions that affect the transport of sperm from the testes through the reproductive tract, such as: Sperm Transport Disorders can encompass conditions like obstructive azoospermia, where blockages impede the passage of sperm, or ejaculatory dysfunction, which involves issues with the ejaculation process itself. These disorders can disrupt the normal flow of sperm and require targeted interventions to restore fertility.
‣ Obstructive azoospermia:
Blockages in the reproductive tract that prevent sperm from being ejaculated. Obstructive azoospermia occurs when blockages within the male reproductive tract hinder the normal ejaculation of sperm.
‣ Ejaculatory dysfunction:
Problems with ejaculation, include retrograde ejaculation (where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting the penis) or premature ejaculation. Ejaculatory dysfunction can significantly impact male fertility by disrupting the normal process of semen release, leading to difficulties in achieving conception.
3. Hormonal Imbalances:
Hormonal imbalances can disrupt the finely-tuned hormonal cascade crucial for proper sperm production and function. Conditions such as hypogonadism or hyperprolactinemia can significantly impact male fertility by altering testosterone levels and other reproductive hormones. Disorders that affect hormonal regulation, including:
‣ Hypogonadism:
Low production of testosterone, which can affect sperm production. Hypogonadism, characterized by low testosterone levels, can disrupt the hormonal balance necessary for optimal sperm production and maturation.
‣ Hyperprolactinemia:
High levels of prolactin, which can interfere with reproductive hormones. Hyperprolactinemia, often caused by pituitary gland abnormalities, can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance necessary for normal reproductive function, potentially leading to infertility in men.
4. Genetic Disorders:
Genetic abnormalities that affect sperm production, sperm function, or reproductive anatomy. Genetic disorders affecting male fertility can encompass a wide range of conditions, from chromosomal abnormalities to single-gene mutations. These genetic abnormalities may disrupt various aspects of sperm production, including spermatogenesis, sperm motility, and sperm morphology. Additionally, some genetic disorders can affect the development and function of reproductive organs, leading to structural abnormalities that impair fertility.
5. Lifestyle Factors:
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in male fertility, with habits such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding excessive alcohol and tobacco consumption positively impacting reproductive health. Additionally, managing stress levels and ensuring adequate sleep can also contribute to optimizing male fertility. Certain lifestyle choices can impact male fertility, including:
‣ Substance abuse:
Alcohol, tobacco, and recreational drugs can affect sperm quality and quantity. Substance abuse can lead to hormonal imbalances and oxidative stress, further compromising male fertility.
‣ Obesity:
The generation of sperm and hormone levels might be affected by excess body weight. Additionally, obesity has been linked to increased inflammation and oxidative stress, further compromising sperm quality and fertility.
‣ Exposure to environmental toxins:
Sperm can be harmed by pesticides, heavy metals, and other environmental contaminants. Additionally, certain occupational exposures, such as working with chemicals or radiation, can also negatively impact sperm health and fertility.
6. Medical Conditions and Treatments:
Medical conditions and treatments can significantly impact male fertility. Certain illnesses and therapies, such as chemotherapy or radiation for cancer, may temporarily or permanently affect sperm production and quality. Certain medical conditions and treatments can affect male fertility, such as:
‣ Varicocele:
Varicocele, the most common reversible cause of male infertility, can lead to impaired sperm production and function due to increased testicular temperature and venous pressure. Swelling of veins in the testes.
‣ Infections:
Infections can disrupt male fertility by causing inflammation and damage to the reproductive organs, potentially leading to scarring and obstruction of the reproductive tract—sexually transmitted infections or other infections that affect the reproductive system.
‣ Cancer and its treatments:
Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery can damage sperm production. Additionally, cancer treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery can adversely impact sperm production and quality, potentially leading to temporary or permanent infertility.
‣ Medications:
Some medications can interfere with sperm production or function. Additionally, certain medications, such as anabolic steroids and some antidepressants, have been associated with decreased sperm production or impaired sperm function.
Each case of male infertility may involve a combination of these factors and types of male infertility, and a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Is male infertility permanent?
One pressing question among individuals grappling with male infertility, is male infertility permanent? While the answer varies depending on the underlying cause, male infertility is not always irreversible. In many cases, lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, or assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can help overcome infertility hurdles. However, prompt diagnosis and timely intervention are crucial in optimizing treatment outcomes.
Conclusion:-
Male infertility is a complex and multifaceted issue with far-reaching implications for individuals and couples alike. By understanding male infertility symptoms, causes, and treatment options, individuals can empower themselves to make informed decisions and seek timely interventions when needed. Whether addressing hormonal imbalances, genetic predispositions, or lifestyle factors, proactive management strategies can often yield favorable outcomes. With the support of knowledgeable healthcare providers specialized fertility centers and the best Gynecologist in Ahmedabad, like Nimaaya IVF Center, couples can navigate the challenges of male infertility with resilience and hope, ultimately realizing their dream of parenthood.