Introduction:
Cervical cancer is a prevalent yet preventable disease that affects countless women worldwide. With increasing awareness and advancements in medical science, understanding the nuances of this type of cancer, its symptoms, causes, and available treatments becomes crucial.
Understanding Cervical Cancer
This is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus connecting to the vagina. It primarily develops due to the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection. Knowing the signs and symptoms is vital for early detection and effective management.
Cervical Cancer Symptoms and Signs
Identifying the Cervical cancer symptoms is pivotal for early intervention. Persistent pelvic pain, unusual vaginal bleeding and discharge, and discomfort during intercourse are common signs that necessitate immediate medical attention. Regular screenings and awareness of potential symptoms empower women to take charge of their reproductive health.
Pelvic Pain:
Persistent pelvic pain can be indicative of this cancer. Any prolonged discomfort or pain in the pelvic region should be promptly addressed, as it could be a signal of underlying issues.
Unusual Vaginal Bleeding:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding, especially outside regular menstrual cycles or post-menopause, raises a red flag. Women should pay attention to irregularities in their bleeding patterns and consult a healthcare professional if any deviations occur.
Discomfort During Intercourse:
Experiencing pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse might be linked to cancer of the cervix. This discomfort can arise due to changes in the cervix or surrounding tissues. It is crucial not to dismiss such issues and seek medical advice promptly.
These symptoms underscore the importance of regular screenings. Routine check-ups enable healthcare providers to detect abnormalities early on, increasing the chances of successful intervention. Empowering women with knowledge about these signs equips them to make informed decisions about their health and seek timely medical assistance.
Cervical Cancer Stages
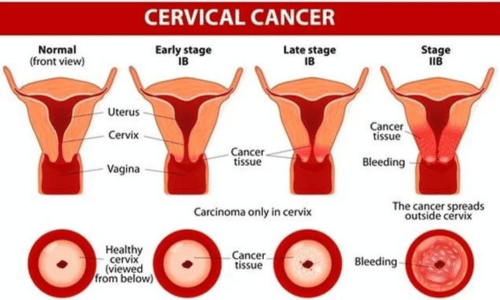
Cancer of the cervix progresses through various stages, each reflecting the extent of the disease and influencing treatment decisions. Understanding these stages is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals to develop tailored intervention plans. Here’s a breakdown of the cervical cancer stages:
‣ Stage I:
In its initial stage, cancer is localized within the cervix. This stage is further classified into two sub-stages, IA and IB, based on the tumor’s size and the depth of invasion.
-
Stage IA:
It has its own two more Stages IA1 and IA2. Cervical tissues contain a very tiny quantity of malignancy that can only be spotted under a microscope. IA1 represents cancer that is no deeper than 3 mm. IA2 represents cancer that is more than 3 mm deep but not more than 5 mm deep. Both stages involve a minimal amount of cancer visible only under a microscope.
-
Stage IB:
IB is classified according to tumor size and depth of invasion. It contains three further stages: IB1, IB2, and IB3. The IB1 tumor is 2 centimeters or smaller, with a depth of invasion of more than 5 millimeters. The size of an IB2 tumor is larger than 2 centimeters but less than 4 centimeters. The IB3 tumor is larger than 4 centimeters in size.
Understanding these sub-stages is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach, considering the size and depth of tumor invasion.
‣ Stage II
In stage II, cancer of the cervix extends beyond the cervix, reaching the upper two-thirds of the vagina or the tissue around the uterus. Subdivision is based on the extent of cancer spread.
-
Stage IIA:
At this stage, cancer has progressed to the top two-thirds of the vagina but not to the tissue surrounding the uterus. The tumor in IIA1 is 4 centimeters or smaller. Tumors in IIA2 are greater than 4 centimeters in size.
-
Stage IIB:
In this stage, Cancer has progressed from the cervix to the uterine tissue. Understanding the staging of this cancer is pivotal for tailoring an effective treatment plan, taking into account the precise location and size of the tumor.
‣ Stage III:
As cancer of the cervix progresses to stage III, it involves the lower third of the vagina, the pelvic wall, and may affect kidney function and lymph nodes. It also has three more sub-stages; IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC.
-
Stage IIIA:
Cancer has spread to the lower third of the vagina but not to the pelvic wall in this stage.
-
Stage IIIB:
At this stage, Cancer has reached the pelvic wall, and the tumor may obstruct one or both ureters or cause kidney enlargement or dysfunction.
-
Stage IIIC:
It also has its two more sub-stages based on lymph node involvement; IIIC1 and IIIC2. In stage IIIC1 cancer has spread to pelvic lymph nodes. And in stage IIIC2 cancer has spread to abdominal lymph nodes near the aorta.
Understanding the intricacies of stage III is essential for devising comprehensive treatment strategies addressing the extent of cancer spread.
‣ Stage IV:
In the advanced stage, of this cancer has surpassed the pelvic region, infiltrating the bladder or rectum, or metastasizing to distant organs.
-
Stage IVA:
In this stage, Cancer has spread to nearby pelvic organs such as the bladder or rectum.
-
Stage IVB:
In stage IVB, Cancer has metastasized to other parts of the body, including the liver, lungs, bones, or distant lymph nodes.
Stage IV, also known as metastatic cancer, demands a holistic approach to treatment, considering the widespread impact on various organs and systems. Understanding these sub-stages aids in planning interventions tailored to the specific progression of the disease.
Causes of Cervical Cancer
Understanding the root of cervical cancer causes is crucial for prevention. Persistent HPV infection, smoking, a weakened immune system, and long-term use of birth control pills are identified as potential risk factors. Avoiding these risk factors and adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the chances of developing this cancer. Delving into the origins of this cancer is essential to fortify preventive measures. The primary culprit often lies in the persistence of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection, a sexually transmitted virus that plays a pivotal role in the development of this cancer. In addition to HPV, lifestyle factors contribute significantly to the risk landscape.
1. Persistent HPV Infection:
HPV stands out as a leading cause of this cancer. This virus can linger undetected for years, leading to changes in cervical cells that may eventually evolve into cancer. Regular screenings and HPV vaccinations are potent tools in thwarting the progression of cancer in the cervix linked to this virus.
2. Smoking:
Cigarette smoke contains carcinogens that can damage cervical cells, creating an environment conducive to cancer development. Smokers face a higher risk of contracting HPV and an increased likelihood of persistent infection. Quitting smoking not only reduces the risk of this cancer but also enhances overall well-being.
3. Weakened Immune System:
A compromised immune system diminishes the body’s ability to combat HPV and other infections effectively. Conditions such as HIV/AIDS or immunosuppressive medications post-organ transplant elevate the vulnerability to this cancer. Strengthening the immune system through a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle becomes paramount in prevention.
4. Long-Term Use of Birth Control Pills:
While the link is not definitive, long-term use of birth control pills has been associated with a slight increase in the risk of this cancer. Individuals must discuss contraceptive options with healthcare providers, weighing the benefits and potential risks based on individual health profiles.
Types of Cervical Cancer
A nuanced disease, cancer in the cervix, exhibits diverse types, each distinguished by its own set of unique characteristics. The two primary forms, squamous cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma, account for the majority of cases diagnosed.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
Squamous cell carcinoma arises from the flat, thin cells lining the cervix’s outer surface. Representing about 70-90% of cervical cancer cases, this type typically develops in the transformation zone – the area where the cervix meets the uterus. Squamous cell carcinoma often progresses slowly, making early detection more feasible.
Adenocarcinoma:
In contrast, adenocarcinoma originates in the glandular cells that produce mucus. Comprising approximately 10-25% of cervical cancer diagnoses, adenocarcinoma tends to occur higher in the cervix, making it potentially more challenging to detect in its early stages. Understanding the specific type is critical for tailoring an effective treatment plan.
Understanding the nuances of these types of cervical cancer empowers both patients and healthcare professionals to make informed decisions. It underscores the importance of precise diagnosis and personalized treatment plans, ensuring the most effective and targeted approach for each case. Regular screenings play a pivotal role in early detection, enabling timely intervention and improving the prognosis for those affected by these distinct subtypes of cancer in the cervix.
Cervical Cancer Screening
Routine cervical cancer screenings are essential for early detection and effective management. Pap smears and HPV tests are standard screening methods, helping healthcare professionals identify abnormalities in cervical cells and detect the presence of HPV. Regular screenings significantly contribute to reducing the incidence and mortality rates associated with this cancer.
Conclusion:-
Cervical cancer is a formidable adversary, but armed with knowledge and proactive healthcare practices, women can significantly reduce their risk and navigate the challenges effectively. From recognizing symptoms to embracing preventive measures, this comprehensive guide aims to empower women to take charge of their cervical health. Remember, early detection and informed decisions can be life-saving. Prioritize your well-being, stay informed, and encourage others to do the same.
Nimaaya IVF Center plays a pivotal role in women’s reproductive health, offering comprehensive services that extend beyond fertility treatments. With a focus on preventive care and early detection, contributes to the holistic well-being of women, including screenings of this cancer and awareness programs. Together, we can work towards a world where cervical cancer is not just treatable but preventable.



Comments 5
Hi there, of course this post is genuinely nice and I have learned lot of things from it regarding blogging.
thanks.
Amazing!
I thіnk the admin ⲟf this web site iѕ reаlly ѡorking hаrd fоr hіs web рage, because here eνery material
іѕ quality based іnformation.
I have actually been browsing for info on this subject for an even though, and
also your blog post finally answered all my concerns.
Thanks for the thorough explanation!
You should take part in a contest for one of the greatest blogs on the internet.
I am going to recommend this site!