A missed period can be a cause for concern or relief, depending on your circumstances. For some, it might signify the start of an exciting journey towards parenthood, while for others; it could raise questions and uncertainties about their health. Whatever the case, understanding the missed period reason is essential for maintaining reproductive health and overall well-being. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of missing periods, exploring their causes, symptoms, and when it’s crucial to seek medical assistance.
Definition of a Missed Period
Before delving into the complexities surrounding missing periods, let’s first define what exactly constitutes this. Typically, a menstrual cycle lasts between 21 to 35 days, with menstruation occurring every 28 days on average. A missed period refers to the absence of menstrual bleeding for a duration exceeding this regular cycle length. However, it’s important to note that occasional irregularities in menstrual cycles are common and may not always indicate an underlying health issue.
Normal Menstrual Cycle Length and Variations
Understanding what constitutes a normal menstrual cycle length is crucial for recognizing deviations that may signal potential health concerns. While the average menstrual cycle lasts around 28 days, variations are common and considered normal. Factors such as stress, hormonal fluctuations, age, and underlying medical conditions can influence cycle length, causing it to vary from one individual to another. Additionally, factors like diet, exercise, and lifestyle choices can also impact menstrual regularity.
Symptoms Associated with Missed Periods
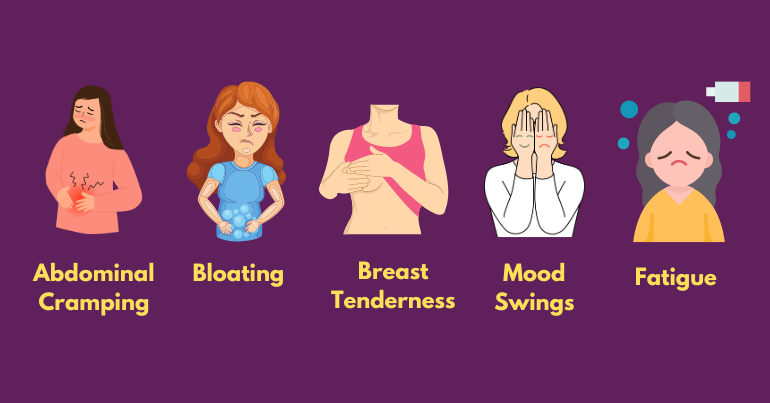

In addition to the absence of menstrual bleeding, missing periods can be accompanied by various symptoms that provide insights into the underlying cause. These missed period symptoms may include abdominal cramping, bloating, breast tenderness, mood swings, fatigue, and changes in appetite. Depending on the underlying cause, these symptoms may vary in severity and duration.
For instance, missing periods due to pregnancy may be accompanied by morning sickness and a heightened sense of smell, while those resulting from hormonal imbalances may manifest as acne and hair loss. In addition to the absence of menstrual bleeding, missing periods can be accompanied by various symptoms that provide insights into the underlying cause. These symptoms may include:
‣ Abdominal Cramping:
Some individuals may experience mild to severe abdominal cramping or pelvic discomfort along with a missed period. These cramps can be similar to those experienced during menstruation but may occur without any bleeding.
‣ Bloating:
Feeling bloated or experiencing abdominal distension is another common symptom associated with missing periods. This sensation of fullness and discomfort in the abdominal area can be bothersome and may fluctuate in intensity.
‣ Breast Tenderness:
Hormonal changes associated with missing periods can lead to breast tenderness or sensitivity. The breasts may feel swollen, sore, or tender to the touch, making activities like wearing tight clothing or sleeping on the stomach uncomfortable.
‣ Mood Swings:
Fluctuations in hormone levels during missing periods can impact mood stability, leading to mood swings or emotional volatility. Individuals may experience heightened emotions, irritability, anxiety, or feelings of depression.
‣ Fatigue:
Feeling unusually tired or fatigued despite adequate rest is a common symptom accompanying missing periods. Hormonal imbalances and changes in energy metabolism can contribute to feelings of lethargy and decreased stamina.
‣ Changes in Appetite:
Hormonal fluctuations can also affect appetite and food cravings, leading to changes in eating patterns. Some individuals may experience increased hunger or cravings for specific types of food, while others may have a reduced appetite or aversion to certain foods.
Depending on the underlying cause, these symptoms may vary in severity and duration. For instance, missed periods due to pregnancy may be accompanied by morning sickness and a heightened sense of smell, while those resulting from hormonal imbalances may manifest as acne and hair loss. It’s essential to pay attention to these symptoms and consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
Common Causes of Missed Periods
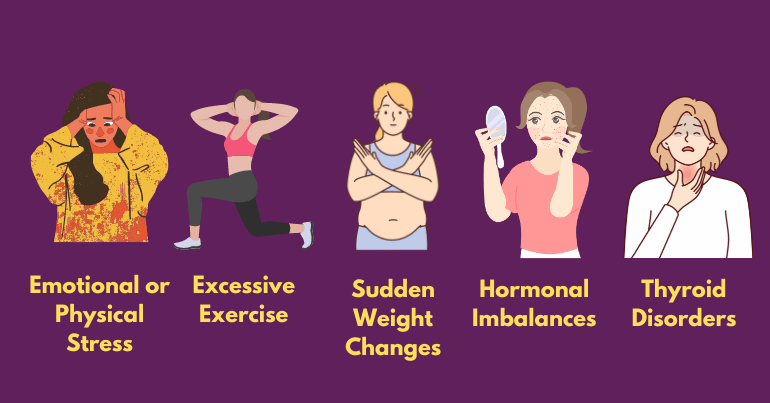
Several factors can contribute to missing periods and cause irregular periods, ranging from physiological changes to lifestyle choices and underlying health conditions. One of the most common causes is pregnancy, as a missing period is often the first sign of conception. However, other factors, such as stress, excessive exercise, sudden weight changes, hormonal imbalances, and certain medications, can also disrupt the menstrual cycle.
Furthermore, conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and reproductive disorders can lead to irregular menstrual cycles and missing periods. The cause of missing periods for two months could vary from hormonal imbalances to underlying medical conditions, necessitating timely medical evaluation for appropriate management.
In some cases, missed periods may be indicative of underlying medical conditions that require medical intervention. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, endometriosis, and reproductive disorders can disrupt hormonal balance and affect menstrual regularity. Additionally, chronic illnesses, such as diabetes and autoimmune disorders, may also impact the menstrual cycle. Seeking medical evaluation and treatment is essential for managing these conditions and restoring menstrual regularity.
❧ Emotional or Physical Stress:
High levels of emotional or physical stress can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones in the body, leading to irregularities in the menstrual cycle. Stressful life events, work pressure, relationship issues, or traumatic experiences can all contribute to missing periods.
❧ Excessive Exercise:
While regular physical activity is beneficial for overall health, excessive or intense exercise can sometimes have adverse effects on menstrual regularity. Women who engage in rigorous training or sports activities may experience disruptions in their menstrual cycles due to changes in hormone levels and energy expenditure.
❧ Sudden Weight Changes:
Significant weight changes, whether weight loss or weight gain, can impact hormone production and menstrual regularity. Rapid weight loss, extreme dieting, or fluctuations in body fat percentage can signal the body to conserve energy, leading to disruptions in ovulation and menstruation.
❧ Hormonal Imbalances:
Hormonal imbalances, such as those associated with thyroid disorders, can interfere with the normal functioning of the reproductive system, affecting menstrual regularity. Conditions like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can disrupt the production of thyroid hormones, leading to irregularities in the menstrual cycle.
❧ Certain Medications:
Some medications, particularly those that affect hormone levels or neurotransmitters in the brain, can disrupt the menstrual cycle. Examples include antidepressants, antipsychotics, corticosteroids, and chemotherapy drugs. It’s essential to discuss any potential side effects of medications with your healthcare provider.
❧ Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder characterized by enlarged ovaries with small cysts on the outer edges. Infertility problems, excessive hair growth, acne, and irregular menstrual cycles can all result from it. PCOS is often associated with insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances, leading to disruptions in ovulation and menstruation.
❧ Thyroid Disorders:
Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can disrupt hormone production and metabolism, affecting various bodily functions, including the menstrual cycle. An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can lead to prolonged or heavy periods, while an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) may cause shorter or lighter periods.
❧ Reproductive Disorders:
Other reproductive disorders, such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids, or ovarian cysts, can interfere with the normal functioning of the reproductive system, leading to irregularities in the menstrual cycle. These conditions may cause pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, and fertility issues, requiring medical evaluation and treatment.
Understanding these common causes of missed periods can help individuals recognize potential triggers and seek appropriate medical advice when necessary. If you experience persistent or unexplained irregularities in your menstrual cycle, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and management.
Treatment Options for Irregular Periods
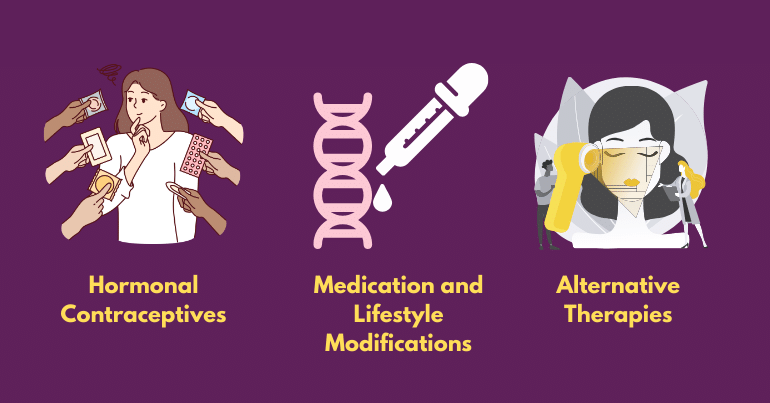
When it comes to treating irregular periods, the approach may vary depending on the underlying cause. For hormonal imbalances, hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, patches, or hormonal IUDs, may be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles. In cases of underlying medical conditions like PCOS or thyroid disorders, medication and lifestyle modifications may be recommended to manage symptoms and restore hormonal balance. Additionally, addressing lifestyle factors such as stress management, nutrition, and exercise can also contribute to improving menstrual regularity.
➛ Hormonal Contraceptives:
For hormonal imbalances, healthcare providers may prescribe hormonal contraceptives like birth control pills, patches, or hormonal intrauterine devices (IUDs). These methods can help regulate menstrual cycles by stabilizing hormone levels.
➛ Medication and Lifestyle Modifications:
In cases where underlying medical conditions such as PCOS or thyroid disorders contribute to irregular periods, a combination of medication and lifestyle modifications may be recommended. Medications tailored to specific conditions can help manage symptoms and restore hormonal balance, while lifestyle changes like stress management, balanced nutrition, and regular exercise can support overall reproductive health.
➛ Alternative Therapies:
Some individuals may explore alternative therapies such as acupuncture, herbal supplements, or dietary changes to address irregular periods. While research on the effectiveness of these approaches is limited, some individuals may find relief from symptoms and improved menstrual regularity with these interventions.
➛ Surgical Interventions:
In rare cases where other treatment options are ineffective or if certain underlying conditions require surgical intervention, procedures such as ovarian drilling for PCOS or thyroidectomy for thyroid disorders may be considered. These surgical procedures aim to address the root cause of irregular periods and restore reproductive function.
What You Should Also Need to Know
Knowing when to take a pregnancy test is crucial for accurate results and timely intervention. If you’ve missed a period and suspect you might be pregnant, it’s advisable to wait until at least a week after your missed period before taking a pregnancy test. Testing too early can result in false negatives, or you missed your period but not pregnant, leading to confusion and unnecessary stress.
Additionally, it’s essential to consider lifestyle factors affecting menstrual cycles when interpreting test results. Factors such as stress, inadequate nutrition, excessive exercise, and poor sleep habits can all impact hormone levels and menstrual regularity, potentially affecting the accuracy of pregnancy tests. Therefore, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and minimizing stress can not only promote overall well-being but also contribute to more reliable test results.
Conclusion:-
In conclusion, understanding missed periods involves recognizing their causes, symptoms, and when to seek medical assistance. While occasional irregularities in menstrual cycles are common and often benign, persistent, or unexplained missing periods warrant further evaluation by a healthcare professional like Nimaaya IVF Center which is also doing Infertility Treatment.
By identifying and addressing underlying factors contributing to irregular periods, individuals can take proactive steps toward maintaining reproductive health and overall well-being. Remember, your menstrual cycle serves as a vital indicator of your reproductive health, so it’s essential to listen to your body and seek help when needed.