Introduction
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder that affects many women of reproductive age. Despite its prevalence, PCOS remains a complex and often misunderstood condition. One of the key challenges in managing PCOS is understanding its different variants. This blog will delve into the various PCOS types, exploring their unique characteristics, PCOS types and symptoms, and available treatments, to help you gain a clearer understanding of this multifaceted syndrome.
What is PCOS?
PCOS, or Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, is a hormonal disorder characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries. Women with PCOS may experience a range of symptoms, including weight gain, acne, hirsutism (excessive hair growth), and infertility. Understanding the different PCOS types is crucial for effective management and treatment.
The Different Types of PCOS
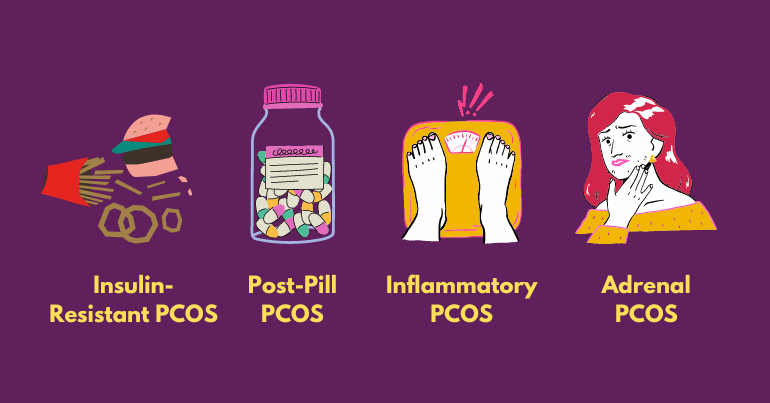
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex and multifaceted endocrine disorder that affects millions of women worldwide. Despite its prevalence, PCOS remains a challenging condition to diagnose and manage due to its diverse presentation. Understanding the different types of PCOS is crucial for effective treatment and management. In this article, we will explore the various PCOS types, the types of cysts associated with PCOS, and the tests used to diagnose this condition.
❧ Insulin-Resistant PCOS:
Insulin-resistant PCOS is the most common type, often linked with metabolic issues. In this form, the body’s cells become resistant to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels and increased insulin production. This excess insulin stimulates the ovaries to produce more androgens, which can disrupt normal ovulation.
Women with insulin-resistant PCOS typically experience weight gain, particularly around the abdomen, and may find it challenging to lose weight. Other symptoms include dark patches of skin (acanthosis nigricans), fatigue, and irregular menstrual cycles. Managing this type of PCOS often involves lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise to improve insulin sensitivity. Medications like metformin are commonly prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels, and hormonal birth control can be used to regularize menstrual cycles.
❧ Post-Pill PCOS
Post-pill PCOS occurs in women who have recently discontinued hormonal birth control. The synthetic hormones in birth control pills can suppress natural hormone production, and stopping the pills can lead to a temporary imbalance. This results in a surge of androgens, causing PCOS-like symptoms.
Women with post-pill PCOS may experience irregular periods, acne, and changes in hair growth patterns after stopping birth control. This type of PCOS is often temporary, and the body may adjust naturally over time. However, some women might require hormonal treatments to balance their androgen levels or lifestyle modifications to support hormone regulation.
❧ Inflammatory PCOS
Inflammatory PCOS is characterized by chronic inflammation, which can lead to elevated androgen levels and ovarian dysfunction. This inflammation can be due to various factors, including stress, environmental toxins, and diet. Women with this type of PCOS often have markers of inflammation, such as elevated C-reactive protein (CRP).
Symptoms of inflammatory PCOS include unexplained fatigue, skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, headaches, and joint pain. Treatment typically involves adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, incorporating supplements like turmeric and omega-3, and implementing stress management techniques to reduce inflammation.
❧ Adrenal PCOS
Adrenal PCOS is a less common form caused by the overproduction of androgens by the adrenal glands rather than the ovaries. This type is often identified through specific hormonal tests that reveal high levels of DHEA-S, an adrenal androgen, while insulin and glucose levels remain normal.
Women with adrenal PCOS may exhibit symptoms such as high levels of stress-induced symptoms, acne, and irregular menstrual cycles. Treatment focuses on reducing stress through lifestyle changes, such as incorporating stress reduction strategies and adaptogens like ashwagandha to support adrenal health. A balanced diet and regular exercise also play a crucial role in managing this type of PCOS.
Understanding the different PCOS types is pivotal in navigating the complexities of this condition. From insulin-resistant PCOS to adrenal PCOS, each variant presents unique challenges and requires tailored approaches to treatment. By recognizing the symptoms and undergoing appropriate testing, women can work with healthcare professionals to develop personalized strategies for managing their PCOS effectively. With the right support and resources, women with PCOS can take proactive steps toward improving their health and overall well-being.
PCOS Types of Cysts
Understanding the PCOS types of cysts, and the types of ovarian cysts associated with PCOS is essential for comprehending the condition’s pathology. In PCOS, the term “cysts” refers to immature follicles that fail to mature and ovulate, leading to the formation of small, fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries. These are not true cysts but rather follicles that have not developed properly. There are two main types of cysts in PCOS:
☑ Follicular Cysts:
These are the most common and form when the follicle does not release an egg and remains filled with fluid. Follicular cysts are usually harmless and often resolve on their own.
☑ Corpus Luteum Cysts:
These occur after the follicle has released an egg (ovulation) and then seals off, accumulating fluid. These cysts can cause pelvic pain and irregular periods. Identifying the type of cyst present can aid in diagnosing and treating PCOS more effectively.
Common Symptoms of PCOS
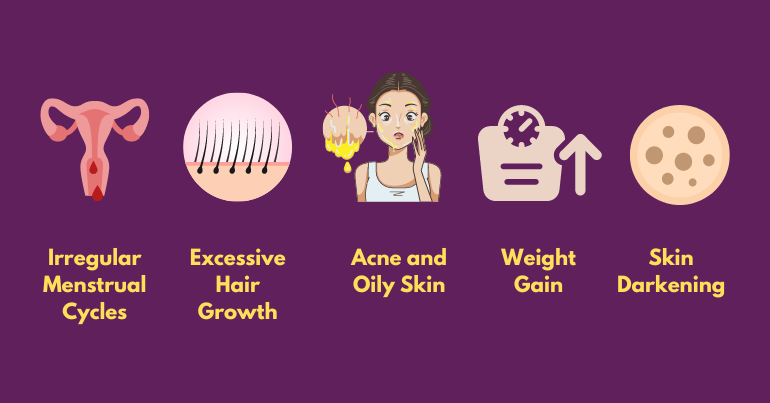
Understanding the symptoms of PCOS is essential for early diagnosis and effective management. While the presentation of symptoms can vary from person to person, there are common signs to be aware of that may indicate the presence of this condition. PCOS symptoms often overlap with other health issues, making it crucial to undergo appropriate testing for accurate diagnosis.
1. Irregular Menstrual Cycles
One of the hallmark symptoms of PCOS is irregular periods, which may manifest as infrequent, absent, or prolonged menstrual cycles. This irregularity is often caused by hormonal imbalances, particularly elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) and insulin resistance.
2. Excessive Hair Growth (Hirsutism)
PCOS can lead to hirsutism, a condition characterized by excessive hair growth on the face, chest, back, or other areas where men typically grow hair. This occurs due to elevated levels of androgens, which stimulate the growth of coarse, dark hair in areas typically associated with male-pattern hair growth.
3. Acne and Oily Skin
Increased androgen levels in PCOS can contribute to the development of acne and oily skin. Hormonal fluctuations disrupt the balance of oil production in the skin, leading to clogged pores, inflammation, and the formation of pimples, blackheads, or cysts.
4. Weight Gain and Difficulty Losing Weight
Many women with PCOS experience weight gain, particularly around the abdomen, despite efforts to maintain a healthy diet and exercise regimen. Insulin resistance, a common feature of PCOS, can contribute to weight gain and make it challenging to lose excess weight.
5. Hair Loss (Male Pattern Baldness)
In addition to excessive hair growth, some women with PCOS may experience male-pattern hair loss or thinning of the scalp hair. This type of hair loss, known as androgenic alopecia, is attributed to the effects of elevated androgens on hair follicles, leading to miniaturization and eventual cessation of hair growth.
6. Skin Darkening (Acanthosis Nigricans)
Acanthosis nigricans is a skin condition characterized by dark, velvety patches that typically appear in body folds and creases, such as the neck, armpits, and groin. It is often associated with insulin resistance and frequently occurs in women with PCOS. This skin disease can be improved by controlling insulin levels with medication and lifestyle modifications.
7. Difficulty Getting Pregnant
One of the main reasons why women cannot conceive is PCOS. Irregular ovulation or anovulation (lack of ovulation) can make it difficult for women with PCOS to conceive naturally. While pregnancy is still possible with PCOS, it may require medical intervention, such as fertility treatments, to improve ovulation and increase the chances of conception.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis. While PCOS can be challenging to manage, early intervention and personalized treatment plans can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall health and well-being. Don’t ignore the signs—take proactive steps to address PCOS and regain control of your health.
Effective PCOS Treatment Options
PCOS treatment aims to manage symptoms, regulate menstrual cycles, and improve fertility outcomes. A comprehensive approach combining lifestyle modifications, medications, and natural supplements is often recommended for optimal results.
‣ Lifestyle Changes:
Diet and exercise play pivotal roles in managing PCOS. Adopting a balanced diet low in processed foods and rich in lean proteins, whole grains, and vegetables can help regulate insulin levels and support weight loss. Regular physical activity, such as cardio and strength training, aids in improving insulin sensitivity and promoting overall health.
‣ Medications:
Various medications are prescribed to address specific symptoms of PCOS and improve overall hormonal balance. Metformin, a commonly prescribed medication, helps improve insulin sensitivity and regulate menstrual cycles. Hormonal birth control, such as combination pills or progestin-only pills, can help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and alleviate symptoms like acne and hirsutism. In cases of infertility, fertility medications like clomiphene citrate or letrozole may be prescribed to induce ovulation and improve the chances of conception.
‣ Natural Supplements:
Several natural supplements have shown promise in managing PCOS symptoms and improving fertility outcomes. Inositol, a type of B vitamin, has been found to improve insulin sensitivity, regulate menstrual cycles, and reduce symptoms like acne and hirsutism. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil supplements, possess anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce inflammation associated with PCOS. Vitamin D supplementation is often recommended, as many women with PCOS are deficient in this essential vitamin, which plays a role in regulating hormone levels and supporting reproductive health.
‣ Holistic Approaches:
In addition to conventional treatments, holistic approaches can complement PCOS management strategies. Stress reduction techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, can help alleviate stress and promote hormonal balance. Acupuncture and traditional Chinese medicine may also be beneficial in regulating menstrual cycles and improving fertility outcomes in women with PCOS.
Effective PCOS treatment encompasses a range of strategies aimed at addressing hormonal imbalances, managing symptoms, and promoting overall health and well-being. By incorporating lifestyle modifications, medications, natural supplements, and complementary therapies, women with PCOS can take proactive steps toward managing their condition and achieving their reproductive goals. Working closely with healthcare providers and adopting a holistic approach to care can empower women with PCOS to take control of their health and lead fulfilling lives.
Testing for PCOS Types
PCOS types test involves a combination of blood tests and imaging studies to assess hormonal levels and ovarian morphology. Blood tests are utilized to measure hormone levels, including testosterone, LH, FSH, and insulin, which can help identify hormonal imbalances characteristic of PCOS and differentiate between the various types. Additionally, transvaginal ultrasound imaging is often performed to visualize the ovaries and identify the presence of cysts. While the term “polycystic” implies the presence of multiple cysts, not all women with PCOS will have visible cysts on ultrasound. These diagnostic tools are essential for accurately diagnosing PCOS and determining the appropriate treatment approach based on the specific type and individual symptoms.
PCOS and Female Infertility
PCOS is one of the leading causes of female infertility due to irregular ovulation or anovulation (absence of ovulation). Women with PCOS often struggle with conceiving naturally. However, there are numerous treatment options available, ranging from lifestyle modifications to fertility treatments. For many women, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and diet can significantly improve ovulation regularity. Additionally, medications like clomiphene citrate or letrozole are often prescribed to stimulate ovulation. In more complex cases, assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended to enhance the chances of conception.
Conclusion:-
Understanding the different PCOS types is fundamental to managing this complex condition effectively. Each type of PCOS requires a unique approach to treatment, making it essential to recognize the specific symptoms and underlying causes. By seeking expert care, such as from the best gynecologist in Vadodara or specialized centers like Nimaaya IVF Center, women with PCOS can achieve better health outcomes and improve their chances of overcoming infertility challenges. Through a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and natural supplements, managing PCOS and its symptoms becomes a more attainable goal.