Introduction
Tubectomy is a surgical procedure aimed at permanent female sterilization. To stop eggs from entering the uterus for fertilization entails closing or restricting the fallopian tubes. This method of contraception has gained popularity due to its effectiveness, low failure rate, and minimal impact on a woman’s hormonal balance. Understanding the procedure of tubectomy, its benefits, and potential side effects, and comparing it with other sterilization methods like vasectomy is essential for making an informed decision about reproductive health.
What is Tubectomy?
The term “tubectomy” refers to the surgical intervention targeting a woman’s fallopian tubes. Tubectomy meaning; that during a tubectomy operation, a surgeon will either cut, tie, or seal these tubes, ensuring that sperm cannot reach an egg for fertilization. This procedure is also known as tubal ligation and is one of the most commonly performed sterilization techniques worldwide.
Benefits of Tubectomy
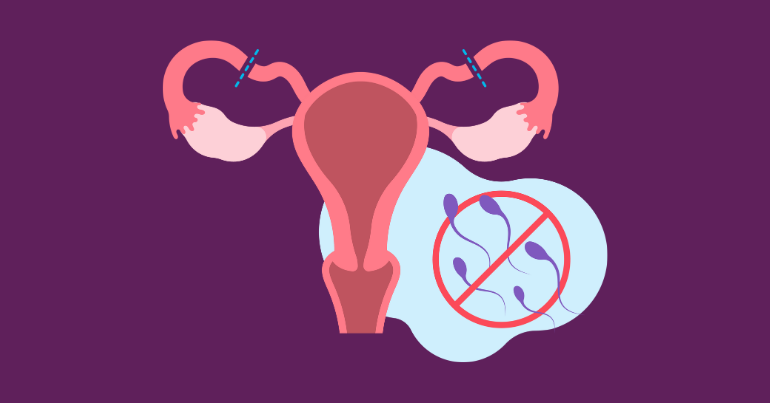
Tubectomy, also known as tubal ligation or female sterilization, is a permanent method of contraception where a woman’s fallopian tubes are surgically cut, tied, or blocked to prevent pregnancy. This procedure offers several benefits:
1. Highly Effective Contraception
Tubal sterilization is one of the most effective forms of birth control, with a success rate of over 99%. Once the procedure is done, it provides lifelong protection against pregnancy without the need for ongoing contraceptive measures. Unlike temporary methods that require regular attention, such as birth control pills or condoms, tubectomy offers peace of mind with its permanent solution. This high level of effectiveness makes it an attractive option for women who seek a reliable and enduring form of contraception.
2. Permanent Solution
Tubal sterilization is a permanent option for women who are confident they do not want to have any more children. It does away with the necessity for other forms of contraception that need to be used and monitored regularly, including pills, patches, or intrauterine devices (IUDs).
3. No Hormonal Side Effects
Unlike hormonal contraceptives (such as birth control pills, injections, or implants), this does not involve the use of hormones, thus avoiding potential side effects like weight gain, mood swings, or increased risk of certain health conditions. This natural approach allows the body’s hormonal system to function normally without interference. As a result, women can maintain their regular menstrual cycles and avoid the complications associated with hormonal contraceptives.
4. Cost-Effective Over Time
Although the initial cost of tubal sterilization may be higher than other contraceptive methods, it can be more cost-effective in the long run as it eliminates the need for ongoing expenses related to other forms of birth control. Additionally, it reduces the financial and logistical burden of managing and purchasing regular contraceptive supplies or medications.
5. Minimal Long-Term Health Risks
This sterilization is generally considered safe, with minimal long-term health risks. Complications from the surgery are rare, and recovery times are relatively short. Most women can resume their normal activities within a week, and the risk of serious complications is extremely low.
6. Immediate Effectiveness
Tubal sterilization is effective immediately after the procedure. Unlike some contraceptives that may require a waiting period before they become fully effective, this sterilization provides instant protection against pregnancy. This immediate effectiveness allows women to have peace of mind right from the moment they leave the operating room. There is no need for additional contraception or the concern of an unintended pregnancy in the interim period.
7. Sexual Freedom
With the worry of unwanted pregnancy removed, many women and their partners find that their sexual relationships improve. There is no need to interrupt sexual activity to use contraceptives, and the fear of contraceptive failure is eliminated.
8. Reduced Risk of Ovarian Cancer
Some studies suggest that tubal sterilization may lower the risk of ovarian cancer. The procedure can prevent cancerous cells from spreading from the ovaries to other parts of the reproductive system. By interrupting the pathway of the fallopian tubes, this sterilization may reduce the chances of cancerous cells migrating, thereby lowering overall cancer risk. This potential benefit adds an important dimension to the decision-making process for women considering tubal sterilization as a permanent birth control method.
While tubectomy has many benefits, it is important to consider that it is a permanent procedure and is generally recommended for women who are certain they do not want any more children. It is also essential to discuss the decision with a healthcare provider to understand the procedure, and potential risks, and to ensure it aligns with the individual’s long-term reproductive goals. Tubal sterilization offers a highly effective, permanent, and convenient method of contraception with several health and lifestyle benefits. However, like any medical procedure, it requires careful consideration and consultation with a healthcare professional.
Understanding the Procedure of Tubectomy
The tubectomy procedure, also known as tubal ligation or female sterilization, is a surgical method of contraception aimed at permanently preventing pregnancy. Here’s an overview of the tubectomy operation and procedure:
1. Pre-Procedure Preparation:
Before undergoing tubal sterilization, the patient typically undergoes a thorough medical evaluation and consultation with a healthcare provider. This is to ensure that tubal sterilization is the most suitable option for contraception and to discuss any potential risks or complications.
2. Anesthesia:
The procedure of tubal sterilization can be performed under general anesthesia, which means the patient is unconscious during the surgery, or under local anesthesia, where only the surgical area is numbed. The choice of anesthesia depends on various factors, including the patient’s medical history and preferences.
3. Incision or Access Point:
The surgeon makes one or more small incisions in the abdomen, usually near the navel, to access the fallopian tubes. In some cases, laparoscopic techniques are used, where a thin, flexible tube with a camera (laparoscope) is inserted through a small incision, allowing the surgeon to view the internal organs on a monitor.
4. Tubal Occlusion:
Once the fallopian tubes are accessed, the surgeon proceeds to occlude, or block, them. This can be achieved through various methods, including Clipping or Banding, Cutting and Tying, and Burning or Cauterization. Small clips or bands are placed across the fallopian tubes to block the passage of eggs. Heat or electrical energy is used to burn or seal the fallopian tubes shut. A section of each fallopian tube is surgically removed, and the ends are tied or sealed to prevent the eggs from traveling through the tubes.
5. Closure:
After the fallopian tubes are occluded, the incisions are closed using sutures or surgical staples. If laparoscopic techniques are used, the incisions are typically small and may not require stitches.
6. Recovery:
Following the procedure of this sterilization, the patient is usually monitored in a recovery area until the effects of anesthesia wear off. Pain medication may be prescribed to manage any discomfort, and the patient is advised to rest and avoid strenuous activities for a few days. Most women can resume normal activities within a week or two.
7. Follow-Up:
After this sterilization, the patient may have a follow-up appointment with their healthcare provider to ensure proper healing and discuss any concerns or questions. The patient needs to adhere to any post-operative instructions provided by their healthcare team.
The tubectomy procedure is a safe and effective method of permanent contraception for women who have decided to no longer have children or do not wish to pursue other forms of birth control. However, like any surgical procedure, it carries some risks, and individuals considering tubal sterilization should thoroughly discuss their options with a healthcare provider.
Side Effects of Tubectomy
Like any surgical procedure, tubal sterilization has potential side effects and risks. Some common side effects include pain at the incision site, fatigue, and slight bleeding. More severe complications, although rare, can include infection, damage to surrounding organs, or adverse reactions to anesthesia. It’s crucial to discuss these potential risks of tubectomy side effects with a healthcare provider before undergoing the procedure.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
Postoperative care is crucial for a smooth recovery. Immediately after the surgery, it’s important to rest and avoid strenuous activities. Prescription drugs can help control pain and discomfort. Maintaining good hygiene and monitoring the incision sites for signs of infection are essential. Follow-up appointments with your doctor will ensure that you are healing properly and can resume normal activities.
Tubectomy vs. Vasectomy
When considering permanent contraception, it’s important to understand the differences between vasectomy and tubectomy. Both procedures are designed to prevent pregnancy permanently, but they target different parts of the reproductive system. A vasectomy is a procedure for men where the vas deferens are cut or sealed to prevent sperm from reaching the semen. In contrast, a tubectomy in female patients involves blocking the fallopian tubes. While both are highly effective, the recovery time and risks may differ slightly, with tubal sterilization being slightly more invasive due to the need for abdominal surgery.
Tubectomy in Female
Tubectomy is specifically designed for females, and it is crucial to understand its implications fully. This procedure is suitable for women who have decided not to have more children or those for whom pregnancy poses health risks. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss all available options and ensure that tubal sterilization is the best choice based on individual circumstances and medical history.
Conclusion:-
Tubectomy provides a reliable, permanent solution for women seeking to control their reproductive futures. Understanding the procedure, benefits, and potential side effects, and comparing it to other methods like vasectomy can help in making an informed decision. The expertise offered by centers like Nimaaya IVF Center ensures that women receive the highest standard of care before, during, and after the procedure. Whether you’re considering tubal sterilization for personal, medical, or economic reasons, it’s important to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure it’s the right choice for you.
-: FAQs:-
Are there any age restrictions for undergoing tubectomy?
Age restrictions for tubectomy may vary depending on regional guidelines and individual healthcare providers’ policies. In some cases, healthcare providers may require individuals to be of a certain age or have completed their families before considering tubectomy as an option. It’s essential to discuss any age-related considerations with your healthcare provider.
Is Tubectomy Reversible?
While tubectomy is considered a permanent method of contraception, some women may inquire about the possibility of reversal in the future. It’s essential to discuss the permanence of tubal sterilization with a healthcare provider before undergoing the procedure.
Can I undergo a tubectomy if I have endometriosis?
Women with endometriosis can often undergo tubal sterilization safely. However, it’s essential to discuss your medical condition and any potential risks with your healthcare provider before proceeding with the procedure.
Will tubectomy affect my menstrual cycle?
Tubectomy does not typically affect menstrual cycles or hormonal balance since it does not involve the use of hormones. Women can expect their menstrual cycles to continue as usual after the procedure.
Is tubectomy covered by insurance?
In many cases, tubectomy is covered by insurance as it is considered a preventative health measure. However, coverage may vary depending on insurance providers and individual policies. For more information, it’s advised to speak with your insurance company.
How soon after tubectomy can I resume sexual activity?
Most women can resume sexual activity within a few days to a week after tubectomy, depending on individual recovery time and comfort levels. However, it’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations and avoid strenuous activity during the initial healing period.
Can I undergo a tubectomy if I’ve had multiple cesarean sections?
Yes, tubectomy can often be performed safely after cesarean sections. However, it’s crucial to discuss your medical history and any previous surgeries with your healthcare provider to ensure that tubal sterilization is appropriate for you.