Introduction
Imagine the joy of anticipating motherhood, only to be met with the heartbreak of infertility. For many women, this is a harsh reality due to blocked fallopian tubes. These vital structures are essential for conception, as they transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus. When blocked, they prevent the sperm from reaching the egg, leading to infertility. Understanding blocked fallopian tubes symptoms can help in early diagnosis and treatment, offering hope to many women striving to conceive. In this article, we will explore the blocked fallopian tubes symptoms, causes, and treatments associated with blocked fallopian tubes, as well as delve into the anatomy and function of the fallopian tubes.
What are Blocked Fallopian Tubes?
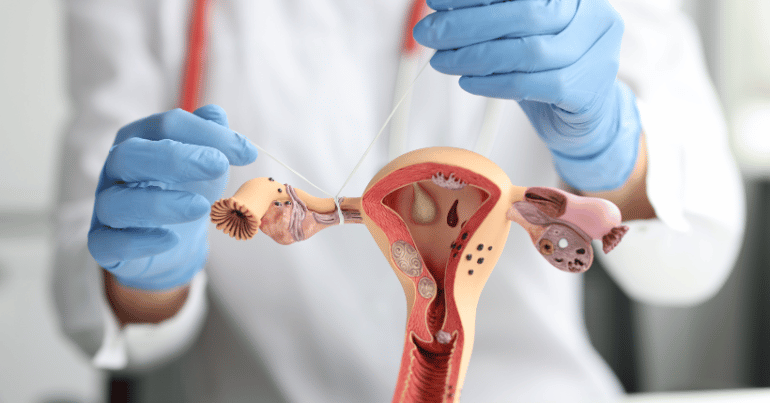
Before diving deep into blocked fallopian tubes, we need to know what the fallopian tube is. Understanding what a fallopian tube is and its function can shed light on how blockages can impact fertility. A blocked fallopian tube occurs when an obstruction prevents the egg from traveling down the tube. This blockage can happen in one or both tubes and can be caused by various factors such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), endometriosis, or previous surgeries. It is crucial to identify the blocked fallopian tube symptoms early to seek appropriate treatment.
Blocked Fallopian Tubes Symptoms
• Pelvic Pain:
One of the most common blocked fallopian tubes symptoms is recurring pelvic pain. This pain is often concentrated on one side of the pelvis and can be mistaken for menstrual cramps or ovulation pain. Chronic pelvic pain, especially if it worsens during menstruation, may indicate fallopian tube blockage.
• Irregular Menstrual Cycles:
Women with blocked fallopian tubes might experience irregular menstrual cycles. This irregularity can be due to underlying conditions such as endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which are known to cause fallopian tube blockages.
• Painful Periods:
Dysmenorrhea, or painful periods, can also be a symptom of blocked fallopian tubes. The pain may be more intense and last longer than typical menstrual cramps, often indicating underlying issues with the reproductive organs.
• Pain During Intercourse:
Dyspareunia, or pain during sexual intercourse, can be a symptom of blocked fallopian tubes. This pain is usually deep within the pelvis and may be caused by conditions that lead to blockages, such as endometriosis or PID.
• Infertility:
Difficulty conceiving after trying for an extended period is a significant symptom of blocked fallopian tubes. Since the fallopian tubes are essential for the egg and sperm to meet, any blockage can prevent natural conception.
• Ectopic Pregnancy:
A blocked fallopian tube can cause an ectopic pregnancy, where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in the fallopian tube itself. This condition is a medical emergency and presents symptoms such as sharp pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding, and dizziness.
Understanding blocked fallopian tubes symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. Recognizing recurring pelvic pain, irregular menstrual cycles, painful periods, pain during intercourse, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy can help in seeking appropriate medical care and improving reproductive health.
Causes of Blocked Fallopian Tubes
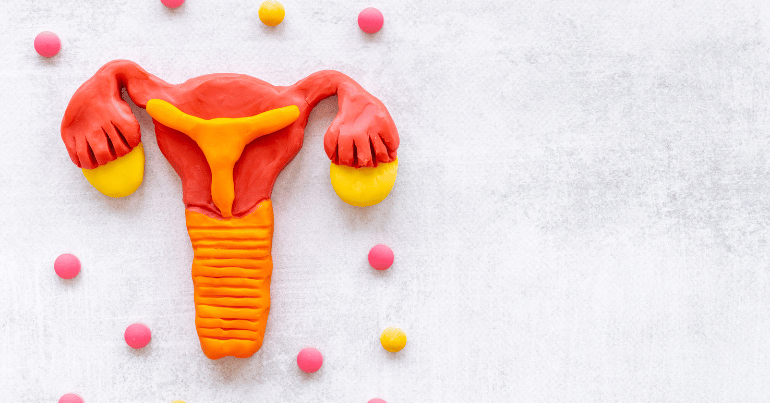

Blocked fallopian tubes can result from various conditions, significantly impacting a woman’s fertility. Common causes include pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which leads to scarring and damage due to infection; endometriosis, where uterine tissue grows outside the uterus, causing adhesions and blockages; and previous surgeries in the pelvic area, which can result in scar tissue formation. Other factors include tubal ligations intended for sterilization, which might inadvertently cause blockages, and genital tuberculosis, which can severely damage the fallopian tubes. Early diagnosis and treatment of these conditions are essential to prevent and manage blockages effectively.
Treatment Options for Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Blocked fallopian tubes can be a significant obstacle for women trying to conceive, as they prevent the sperm and egg from meeting. Understanding the available treatment options is crucial for addressing this condition and improving fertility. Here we will explore various fallopian tube blockage treatments and related issues such as fallopian tube cysts and infections.
1. Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat blocked fallopian tubes. During the surgery, a small camera (laparoscope) is inserted into the pelvic cavity to identify and remove blockages, scar tissue, or other obstructions.
2. Tubal Cannulation
Tubal cannulation involves using a catheter to clear the blockage. This procedure is often done during a hysterosalpingography (HSG) test, where a dye is injected into the uterus and fallopian tubes to detect blockages. If a blockage is found, the catheter can be used to open the tube.
3. Salpingectomy
The surgical excision of one or both fallopian tubes is known as a salpingectomy. This procedure is typically recommended if the blockage is caused by a severe infection or significant damage to the tubes. It can also be done to remove fallopian tube cysts that are causing blockages.
4. Salpingostomy
A salpingostomy is a surgical procedure to create an opening in the fallopian tube to bypass the blockage. This is often used when there is a hydrosalpinx (fluid-filled tube) that needs to be drained.
5. Fimbrioplasty
Fimbrioplasty is a surgical procedure that repairs the fimbriae, the finger-like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes that help guide the egg into the tube. This procedure can be used if the fimbriae are damaged or blocked.
6. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
For women with severe blockages or those who do not respond to surgical treatments, IVF is a viable option. IVF bypasses the fallopian tubes entirely by fertilizing the egg outside the body and then implanting the embryo directly into the uterus.
7. Medications for Infections
If a fallopian tube blockage is due to a fallopian tube infection, antibiotics can be prescribed to treat the infection and reduce inflammation. Antibiotics, however, might not be able to undo any harm or scarring that has already happened.
Blocked fallopian tubes can present a significant challenge for women trying to conceive, but understanding the symptoms and available treatment options can make a significant difference. By recognizing blocked fallopian tubes symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical intervention, women can improve their chances of overcoming infertility. Whether through surgical procedures like laparoscopic surgery, tubal cannulation, and fimbrioplasty, or through assisted reproductive technologies like IVF, there are multiple pathways to achieving a successful pregnancy.
Fallopian Tube Parts and Their Functions
The fallopian tubes play a crucial role in the reproductive system, serving as the passageway for the egg to travel from the ovary to the uterus. Understanding the anatomy and functions of the fallopian tube parts can provide insight into their importance in the process of conception and pregnancy.
• Anatomy of the Fallopian Tubes:
The fallopian tubes are paired structures, each approximately 10-12 centimeters long, extending from the upper corners of the uterus to the ovaries. They consist of four main parts: Infundibulum, Ampulla, Isthmus, and Interstitial (or Intramural) Part. Each of these parts has a specific function in the journey of the egg and the process of fertilization.
1. Infundibulum
The infundibulum is the funnel-shaped, open end of the fallopian tube closest to the ovary. It features finger-like projections called fimbriae that help capture the released egg from the ovary. The infundibulum plays a critical role in ensuring the egg enters the fallopian tube.
Function: The primary function of the infundibulum is to catch and guide the egg into the fallopian tube after ovulation. The fimbriae move rhythmically to create a current that draws the egg into the tube.
2. Ampulla
The ampulla is the widest section of the fallopian tube and the site where fertilization usually occurs. It is located between the infundibulum and the isthmus.
Function: The ampulla provides the environment where the sperm meets and fertilizes the egg. This part of the tube is where the initial stages of embryonic development begin. The ampulla’s ciliated lining helps propel the fertilized egg towards the uterus.
3. Isthmus
The isthmus is the narrow, medial segment of the fallopian tube that connects the ampulla to the interstitial part. It has a thicker muscular wall and a smaller lumen compared to the ampulla.
Function: The isthmus acts as a passage for the fertilized egg as it moves from the ampulla to the uterus. The muscular contractions of the isthmus help propel the embryo through the tube.
4. Interstitial (or Intramural) Part
The interstitial part is the section of the fallopian tube that passes through the muscular wall of the uterus. It is the narrowest segment and opens into the uterine cavity.
Function: This part of the tube ensures the final passage of the fertilized egg into the uterus for implantation. It also plays a role in regulating the timing of the egg’s entry into the uterine cavity.
Fallopian Tube Functions
The fallopian tubes have several essential functions in the reproductive process:
• Transport of the Egg:
The egg is transferred from the ovary to the uterus by the fallopian tubes. The coordinated movements of the fimbriae, cilia, and muscular contractions facilitate this journey.
• Site of Fertilization:
The ampulla of the fallopian tube is the primary site where fertilization occurs. The tube provides a conducive environment for the sperm to meet and fertilize the egg.
• Early Development of the Embryo:
After fertilization, the fallopian tube supports the early stages of embryonic development as the embryo travels towards the uterus.
Fallopian Tube Pregnancy
A fallopian tube pregnancy, also known as an ectopic pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg implants and begins to grow outside the uterus, typically within the fallopian tube. If treatment for this ailment is delayed, it may become fatal.
- Causes: Ectopic pregnancies often result from conditions that damage the fallopian tubes, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), previous surgeries, or congenital abnormalities.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms of this type of pregnancy include sharp pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding, and dizziness. If a fallopian tube pregnancy is suspected, immediate medical attention is crucial.
- Treatment: Treatment options for ectopic pregnancy include medication to stop the growth of the embryo or surgical intervention to remove the ectopic tissue.
Conclusion:
Blocked fallopian tubes can be a significant barrier to conception, but with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many women can overcome this challenge. Understanding the blocked fallopian tubes symptoms, causes, and treatment options for blocked fallopian tubes is essential for anyone experiencing infertility. If you suspect you have blocked fallopian tubes, consult with a specialist like Dr Pooja Nadakarni at Nimaaya IVF Center to explore your options and take the first step towards achieving your dream of motherhood.
Being informed about blocked fallopian tubes symptoms and seeking timely medical intervention can make a significant difference. Whether it’s through surgical procedures or assisted reproductive technologies like IVF, there is hope for women with blocked fallopian tubes to conceive and experience the joy of motherhood.
-:FAQs:-
1) Can I Still Get Pregnant if I Have Blocked Fallopian Tubes?
Answer: Yes, it is possible to get pregnant with blocked fallopian tubes, but it can be challenging. If both tubes are blocked, natural conception is unlikely without medical intervention. Treatments such as laparoscopic surgery to remove the blockage, tubal cannulation, or assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF) can increase your chances of pregnancy.
2) What Are the Main Symptoms That Indicate Blocked Fallopian Tubes?
Answer: Common symptoms of blocked fallopian tubes include recurring pelvic pain, irregular menstrual cycles, painful periods, pain during intercourse, difficulty conceiving, and ectopic pregnancy. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
3) What Causes Fallopian Tubes to Become Blocked?
Answer: Blocked fallopian tubes can result from various factors, including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), endometriosis, previous pelvic surgeries, tubal ligation, or genital tuberculosis. These conditions can lead to scarring, adhesions, or other obstructions that block the tubes.
4) Can Blocked Fallopian Tubes Cause Other Health Issues?
Answer: Yes, blocked fallopian tubes can lead to complications such as ectopic pregnancy, where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube. This is an emergency medical situation that has to be treated immediately. Additionally, underlying conditions causing the blockage, such as PID or endometriosis, can have broader health implications.
5) Is Surgery the Only Option to Treat Blocked Fallopian Tubes?
Answer: Surgery is a common treatment option for blocked fallopian tubes, but it is not the only one. Tubal cannulation, medications to treat infections, and assisted reproductive technologies like IVF are alternative treatments. The best approach depends on the cause and severity of the blockage, as well as individual circumstances.
6) What Should I Expect During Recovery After Surgery for Blocked Fallopian Tubes?
Answer: Recovery after surgery for blocked fallopian tubes, such as laparoscopic surgery, generally involves a few days to a week of rest. You may experience mild discomfort, bloating, or spotting. Your doctor will provide specific post-operative care instructions, including activity restrictions and follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery and discuss further treatment options.
7) Can Blocked Fallopian Tubes Be Prevented?
Answer: While not all causes of blocked fallopian tubes can be prevented, reducing the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) through safe sex practices, timely treatment of infections, and regular gynecological check-ups can help maintain tubal health. Managing conditions like endometriosis and seeking prompt treatment for any pelvic pain or irregularities can also reduce the risk of blockages.