Introduction
Endometrial thickness is a critical factor in women’s reproductive health, influencing everything from menstrual cycles to fertility and pregnancy outcomes. Understanding the nuances of normal and natural endometrium thickness and its variations can provide valuable insights for those navigating the treatment of IVF or dealing with fertility issues. This comprehensive guide will delve into what constitutes a normal endometrial thickness size, explore effective treatment options, and explain the strategies to increase endometrium thickness for IVF. Whether you’re considering pregnancy, undergoing IVF, or seeking expert advice from the best gynecologist in Surat, including renowned centers like Nimaaya IVF Center, understanding endometrial thickness during pregnancy and beyond is essential for optimizing reproductive health.
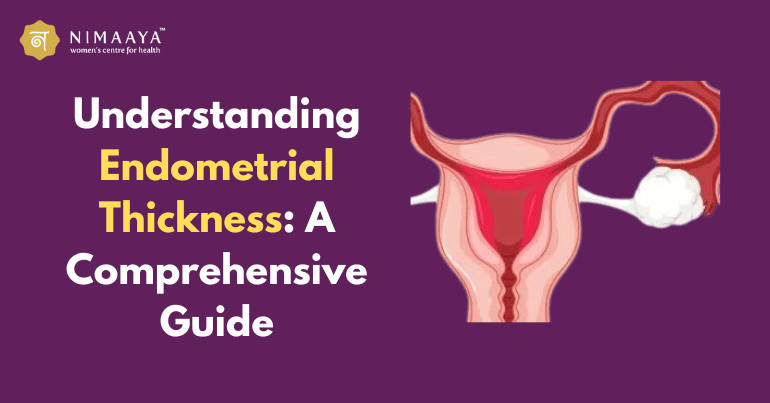
What is Endometrial Thickness?
The measurement of the endometrium, or lining of the uterus, is referred to as endometrial thickness. This lining changes throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle in response to hormonal signals. The thickness is an indicator of the endometrium’s health and its ability to support a pregnancy. It serves as an indicator of the uterine environment’s readiness to support a pregnancy. During the menstrual cycle, estrogen and progesterone levels influence the growth and shedding of the endometrial lining. A thin lining may indicate insufficient hormonal support or other underlying conditions that could hinder fertility. Conversely, an excessively thick endometrial lining might suggest hormonal imbalances or the presence of benign growths like polyps or fibroids.
Significance of Endometrial Thickness
The significance of endometrial or intrauterine thickness lies in its crucial role in reproductive health, particularly during pregnancy. Endometrial thickness during pregnancy is vital for embryo implantation and development. A natural intrauterine thickness size in mm ranges from 7 to 14 mm at the time of implantation, providing an optimal environment for the embryo to attach and grow. This measurement is a key indicator of uterine receptivity and is closely monitored in fertility treatments to enhance pregnancy outcomes. Ensuring the endometrium is within this normal size range can significantly impact the success of conception and the maintenance of a healthy pregnancy.
What is Endometrial Thickness Normal Size?
Endometrial or intrauterine thickness refers to the measurement of the lining of the uterus, known as the endometrium. This thickness varies throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle, responding to hormonal changes and playing a crucial role in menstrual health, fertility, and pregnancy. Understanding the normal size of endometrial or intrauterine thickness is essential for diagnosing and managing various gynecological conditions. Endometrial thickness normal size in mm and in Different Phases:
Menstrual Phase (Days 1-5):
During menstruation, the endometrial lining sheds, resulting in the thinnest cycle measurement, typically around 2-4 mm.
Proliferative Phase (Days 6-14):
As Estrogen levels rise, the endometrium begins to thicken in preparation for potential pregnancy. By the end of this phase, the intrauterine thickness usually ranges from 5-7 mm.
Secretory Phase (Days 15-28):
Following ovulation, the endometrium reaches its maximum thickness, influenced by progesterone. A normal endometrial thickness during this phase is approximately 8-14 mm, creating an optimal environment for embryo implantation.
Understanding these variations in the thickness of intrauterine throughout the menstrual cycle helps healthcare providers assess reproductive health and fertility potential accurately. Regular monitoring and timely intervention ensure optimal endometrial health, contributing to overall well-being and reproductive success.
Ways or Strategies to Enhance Endometrial Thickness for IVF
Enhancing endometrial thickness for IVF is crucial for improving the chances of successful embryo implantation and pregnancy. One effective strategy on how to increase endometrial thickness for IVF is through hormonal therapies, such as Estrogen supplements, which directly stimulate the growth of the endometrial lining. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, including a nutrient-rich diet and regular physical activity, can promote a healthier endometrium. Alternative therapies, like acupuncture, are also believed to enhance blood flow to the uterus, potentially increasing its thickness for IVF. By combining these approaches, women can create a more favorable uterine environment, thus optimizing their IVF outcomes.
Treatment Options for Endometrial Thickness
Endometrial or intrauterine thickness abnormalities can significantly impact a woman’s reproductive health, particularly during pregnancy. Understanding treatment options is essential for managing conditions associated with thick or thin endometrial linings.
Hormonal Therapies:
Hormonal therapies are commonly used to regulate endometrium thickness. In cases of thin endometrial lining, estrogen supplements may be prescribed to promote growth and thickening. Conversely, excessive thickening, as seen in conditions like endometrial hyperplasia, may require progesterone therapy to induce shedding and reduce thickness. These hormonal treatments aim to restore the endometrium to a normal size conducive to pregnancy.
Fertility Treatments:
For women undergoing fertility treatments such as IVF, optimizing the thickness of intrauterine is crucial for successful embryo implantation. In cases of inadequate endometrial thickness, doctors may adjust medication protocols or timing of embryo transfer to enhance the chances of pregnancy. Close monitoring of its thickness during fertility treatments ensures that the uterine environment is optimal for embryo attachment and growth.
Surgical Interventions:
In certain cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address these issues. For example, the removal of uterine polyps or fibroids can help normalize intrauterine thickness and improve fertility outcomes. Additionally, procedures like hysteroscopy allow doctors to directly visualize the uterine lining and perform targeted interventions to address abnormalities contributing to thickening or thinning.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Lifestyle factors, including diet and exercise, can also influence endometrium thickness. Adopting a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports hormonal balance and overall reproductive health. Regular physical activity helps regulate hormones and may contribute to maintaining a healthy endometrial lining. Stress management techniques such as mindfulness and relaxation therapies can also positively impact hormonal balance and intrauterine thickness.
Pregnancy Management:
Monitoring endometrial or intrauterine thickness during pregnancy is essential for assessing the uterine environment and potential risks. A natural intrauterine thickness throughout pregnancy, typically ranging from 7 to 14 mm, supports embryo implantation and fetal development. Close monitoring ensures that abnormalities, such as excessive thickening or inadequate thickness, are promptly addressed to minimize complications and optimize pregnancy outcomes.
Options for endometrial thickness treatment vary depending on the underlying cause and individual circumstances. Hormonal therapies, fertility treatments, surgical interventions, and lifestyle modifications all play crucial roles in managing endometrial thickness abnormalities and optimizing reproductive health. Close collaboration between patients and healthcare providers ensures that treatment plans are tailored to address specific needs and achieve the best possible outcomes for women, particularly during pregnancy.
Impact of Endometrial Thickness on Women’s Health, Fertility, and Menstrual Cycles
Endometrial or intrauterine thickness is a vital aspect of women’s reproductive health, influencing everything from menstrual regularity to fertility and pregnancy outcomes. The endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus, undergoes cyclical changes influenced by hormonal fluctuations throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle. Its thickness can provide essential clues about a woman’s overall reproductive health.
Menstrual Cycles:
During a typical menstrual cycle, the endometrium thickens in response to rising estrogen levels, preparing for potential pregnancy. This process, known as the proliferative phase, sees the endometrial lining grow from a few millimeters to about 6-10 mm. During menstruation, the endometrium sheds if fertilization is unsuccessful. Abnormalities in intrauterine thickness can disrupt this cycle, leading to irregular periods, heavy menstrual bleeding, or amenorrhea (absence of menstruation).
Fertility:
For women trying to conceive, intrauterine thickness is a crucial factor. An adequately thickened endometrium, typically between 8 to 14 mm during the secretory phase, is essential for successful implantation of an embryo. If the lining is too thin, it may not support implantation, leading to difficulties in achieving pregnancy. Conversely, a lining that is too thick can be a sign of endometrial hyperplasia, which can also impede fertility.
Women’s Health:
Beyond fertility and pregnancy, endometrium thickness can indicate broader health issues. A thickened endometrial lining might signal conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), obesity, or hormonal imbalances. Such conditions often require medical intervention to manage and prevent further complications, including the risk of endometrial cancer in cases of untreated hyperplasia.
This thickness profoundly impacts women’s health, fertility, and menstrual cycles. Understanding and monitoring this aspect of reproductive health is crucial for diagnosing and treating various gynecological conditions, enhancing fertility, and ensuring healthy pregnancies. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, undergoing regular check-ups, and seeking expert medical advice when needed, women can manage their endometrial health effectively.
Conclusion:-
Understanding endometrial thickness is essential for women’s health, particularly for those dealing with fertility issues or undergoing IVF treatment. Whether through lifestyle changes, medical interventions, or specialized care at centers like Nimaaya IVF Center, women have multiple options to optimize their endometrial health. Consulting with the Best IVF Center in Surat or a gynecologist can provide personalized advice and treatment plans, ensuring the best possible outcomes for reproductive health and fertility.