Introduction
In the realm of assisted reproductive technology (ART), traditional surrogacy stands out as a unique method where the surrogate mother shares a genetic connection with the child she carries. Unlike gestational surrogacy where the surrogate carries a child conceived through in vitro fertilization (IVF) using the intended parents’ or donor’s genetic material, this type of surrogacy involves the surrogate providing her egg for fertilization. This raises complex ethical and legal questions, particularly regarding parentage and the rights of all involved parties. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of traditional surrogacy, examining its definition, legal status, and the nuances surrounding its practice, with a special focus on traditional surrogacy in India and the services provided by Nimaaya IVF Center.
What is Traditional Surrogacy?
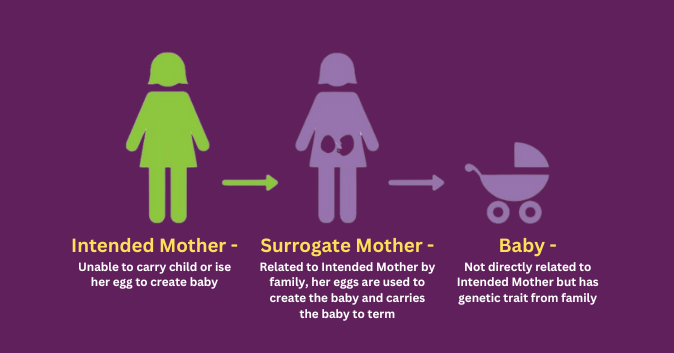
Traditional surrogacy, as defined in assisted reproductive technology, involves a unique arrangement where the surrogate mother shares a genetic connection with the child she carries. In this type of surrogacy, the surrogate mother contributes her egg, which is fertilized with the intended father’s sperm or donor sperm through artificial insemination.
This distinguishes the type of surrogacy from gestational surrogacy, where the surrogate mother carries a child conceived through in vitro fertilization using the egg and sperm of the intended parents or donors. The genetic link between the surrogate mother and the child underscores the complexity and intimacy of authentic surrogacy arrangements, shaping the dynamics of parentage and familial relationships.
Also Read: Surrogacy: A Comprehensive Guide to the Process, Types, and Legal Considerations
How is Traditional Surrogacy Done?
Traditional or authentic surrogacy, unlike gestational surrogacy, involves a more intimate genetic connection between the surrogate mother and the child she carries. In this type of surrogacy, the surrogate mother not only carries the child but also contributes her genetic material, which distinguishes it from other forms of assisted reproduction. This intimate genetic connection underscores the complexities and ethical considerations inherent in authentic surrogacy arrangements. Here’s how this surrogacy is typically done:
❧ Selection of Surrogate:
The process begins with the selection of a suitable surrogate mother. Surrogacy agencies or clinics often facilitate this process, ensuring that the surrogate meets certain criteria such as age, health, and psychological stability. In some cases, the intended parents may choose someone they know personally to be their surrogate.
❧ Medical Evaluation:
Once a surrogate is selected, she undergoes a thorough medical evaluation to assess her reproductive health and ability to carry a pregnancy to term. This evaluation may include physical examinations, blood tests, and screenings for infectious diseases.
❧ Legal Agreements:
All parties’ expectations, rights, and duties are outlined in legal agreements. These contracts typically address issues such as financial compensation, parental rights, and potential risks and liabilities. It’s crucial for both the surrogate and intended parents to have independent legal counsel to ensure their interests are protected.
❧ Artificial Insemination:
Using artificial insemination, the intended father’s or donor sperm fertilizes the surrogate mother’s egg in traditional surrogacy. This procedure can be performed in a clinical setting, usually under the supervision of fertility specialists.
❧ Monitoring and Support:
Throughout the pregnancy, the surrogate mother receives regular medical monitoring and support to ensure her health and the well-being of the developing fetus. This includes prenatal care, ultrasounds, and other necessary medical interventions.
❧ Birth and Parental Rights:
Legal procedures are pursued to establish parental rights at the time of the baby’s birth. Depending on the jurisdiction, the intended parents may need to go through adoption or other legal processes to gain full custody of the child. It’s essential to adhere to the legal requirements of the relevant jurisdiction to avoid any complications later on.
❧ Emotional Support:
This type of surrogacy can be emotionally challenging for all parties involved. Surrogates may experience mixed feelings about giving up the baby, while intended parents may grapple with the complexities of their relationship with the surrogate and the child. Access to counseling and support groups can help navigate these emotional challenges and foster positive relationships among all parties.
❧ Post-Birth Arrangements:
After the birth of the child, arrangements are made for the transfer of parental rights to the intended parents. This may involve legal paperwork and court proceedings, depending on the laws of the jurisdiction. Open communication and cooperation between the surrogate and intended parents are crucial during this transition period.
Traditional or authentic surrogacy involves a series of carefully orchestrated steps, including the selection of a surrogate, medical procedures, legal agreements, and emotional support. While the process may be complex and emotionally demanding, it offers a viable option for individuals and couples seeking to build their families through assisted reproductive technology.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Surrogacy
Traditional surrogacy comes with both advantages and drawbacks that intending parents and surrogates must carefully consider. One of the primary advantages is the genetic connection between the surrogate mother and the child, which can be significant for some intending parents. This connection can create a unique bond and sense of biological continuity. Additionally, traditional surrogacy tends to be less expensive than gestational surrogacy since it doesn’t involve the additional cost of IVF procedures. However, traditional surrogacy also poses significant challenges, particularly in terms of legal and emotional complexities.
The genetic link between the surrogate and the child can lead to complex legal issues regarding parental rights and responsibilities. Moreover, the emotional toll on both the surrogate and the intending parents can be substantial, as the surrogate may struggle with relinquishing the child, and the intending parents may face uncertainty and potential attachment issues. Overall, while traditional surrogacy offers certain benefits, it also requires careful consideration and support to navigate its potential drawbacks.
Ethical Considerations of Traditional Surrogacy
Traditional or customary surrogacy raises profound ethical questions regarding the relationship dynamics between the surrogate mother, the intended parents, and the resulting child. Critics argue that this surrogacy may blur the boundaries between motherhood and contractual agreements, potentially leading to emotional and psychological challenges.
Legal Considerations in Traditional Surrogacy
The legality of traditional surrogacy is a complex issue, particularly in jurisdictions like India where regulations have undergone significant changes. In this situation, couples in India may have this question in their mind, “Is traditional surrogacy legal in India or not?” Legal issues are raised by traditional or customary surrogacy, in which the surrogate mother is genetically related to the child she bears. These issues mostly pertain to parental rights, consent, and the safety of all parties. In India, while this type of surrogacy itself may not be explicitly illegal, commercial surrogacy, including both traditional and gestational, was banned in 2018 to address concerns of exploitation and unethical practices.
This ban has significantly impacted the landscape of surrogacy in India, pushing for a shift towards altruistic surrogacy, where the surrogate is not compensated beyond medical expenses. However, the specific legal framework surrounding traditional surrogacy in India may still be subject to interpretation and may vary depending on regional regulations and judicial rulings. Therefore, individuals considering traditional surrogacy in India must navigate these legal complexities carefully and seek expert legal advice to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Conclusion:-
Traditional surrogacy remains a contentious topic, raising complex issues related to genetics, legality, and ethics. While it offers a unique solution for individuals and couples struggling with infertility or genetic disorders, this surrogacy also presents challenges that require careful consideration and thoughtful regulation. As the landscape of assisted reproductive technology continues to evolve, it is imperative to address the nuances of traditional surrogacy with sensitivity and respect for the rights and well-being of all involved parties.